Fig. 1.
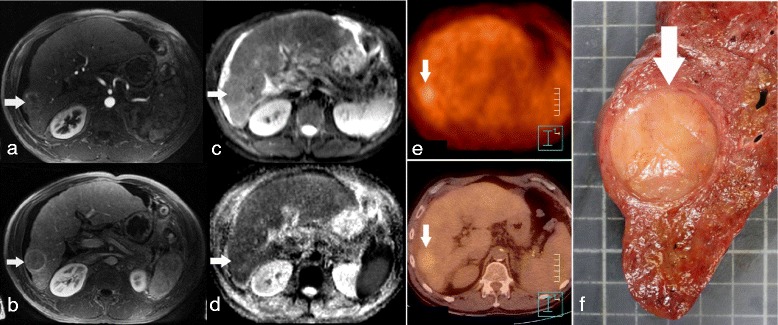
Poorly differentiated HCC in a patient with alcoholic cirrhosis, showing restricted ADC on DWI-MRI and increased uptake on the FDG-PET/CT. Transverse dynamic contrast-enhanced initial post contrast MR image shows a 30 mm large nodular enhancing lesion in the right liver on 3D GE arterial phase imaging (a, arrow) with wash-out on portal-venous phase (b, arrow). The lesion is mildly hyper intense on transverse DW image (b = 800 s/mm2; c, arrow) and has a low ADC (1.06 × 10−3 mm2/s) on the ADC map (d, arrow). FDG-PET/CT shows an increased tumour uptake with a SUVT = 4.1 and SUVT/L = 1.24 (e, arrow). The explanted liver showed an Edmondson-Steiner grade 4 HCC (f, arrow)
