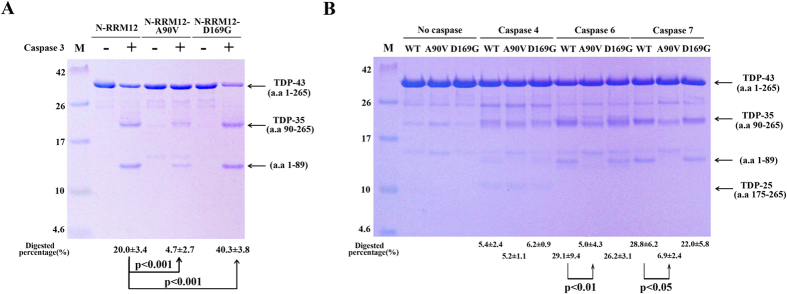
Figure 4. TDP-43 D169G mutant is more susceptible to proteolytic cleavage by caspase 3.
(A) The wild-type, A90V and D169G mutant of TDP-43 (N-RRM12, residues 1–265) were incubated with caspase 3 for two hours. The SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie blue revealed that TDP-43 was cleaved into TDP-35. Tandem mass spectrometry confirmed that caspase 3 digested N-RRM12 into two major fragments, TDP-35 (residues 90–265), and residues 1–89. (B) The wild-type, A90V and D169G mutant of TDP-43 (N-RRM12) were incubated with caspase 4, 6 and 7 for 16 hours. The digested proteins were resolved by 15% Tricine-SDS-PAGE with Coomassie blue staining. The mean percentages with standard errors shown at the bottom of the gel were calculated from three independent experiments. Statistical significance P values were determined by an unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test.