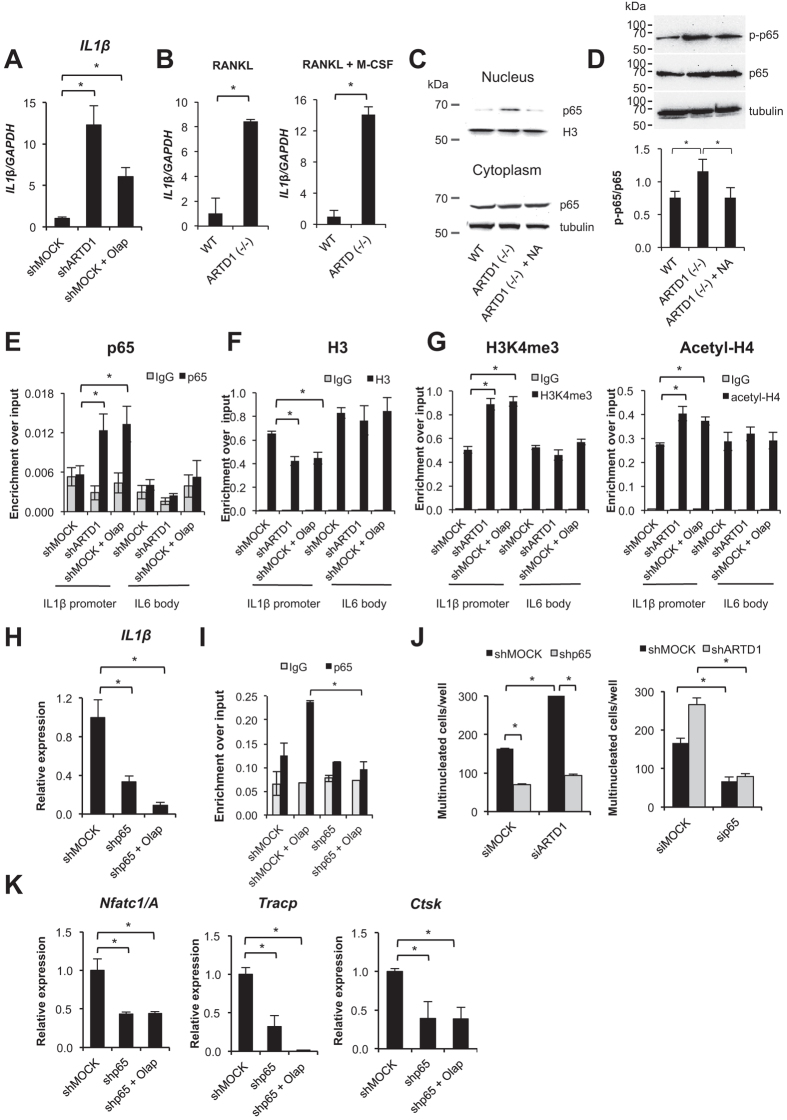
Figure 4. ARTD1 silencing or inhibition of ADP-ribosylation facilitates p65 recruitment to the promoter of IL-1β and chromatin remodelling at this site.
(A) IL-1β expression was compared between 3-day-old osteoclasts derived from shMOCK and shARTD1 RAW264.7 macrophages. (B) The expression of IL-1β was quantified in 3-day-old osteoclasts derived from WT and Artd1 (−/−) BMDM by real-time PCR. (C,D) The activation of NF-κB was analysed by measuring nuclear translocation (C) and Ser536 phosphorylation (D) of p65/RelA in 3-day-old osteoclasts derived from BMDM isolated from WT and Artd1 (−/−) by western blotting. IL-1β neutralizing antibody (NA) was added to the medium of differentiating Artd1 (−/−) every 8 h. (E–G) The association of p65 with the promoter of IL-1β as well as H3 occupancy, H3K4 trimethylation and H4 acetylation was determined by ChIP in RAW 264.7 macrophages-derived osteoclasts differentiated in the presence of RANKL for 72 h. As a negative control, the body of IL6 was used. (H) The expression of IL-1β was compared between 3-day-old osteoclasts derived from shMOCK and shp65 RAW 264.7 macrophages treated or not with olaparib. (I) Recruitment of p65 to the IL-1β promoter was assessed in 3-day-old osteoclasts derived from shMOCK and shp65 RAW 264.7 macrophages treated or not with olaparib. (J) The multinucleation of double-silenced RAW 264.7 macrophages (left panel: siARTD1/shp65, right panel: sip65/shARTD1) was quantified 48 h after induction of the differentiation with RANKL (72 h after cell transfection with siRNA). (K) The expression of osteoclast markers in 3-day-old shMOCK and shp65 ( ± olaparib) osteoclasts was quantified using real-time PCR.