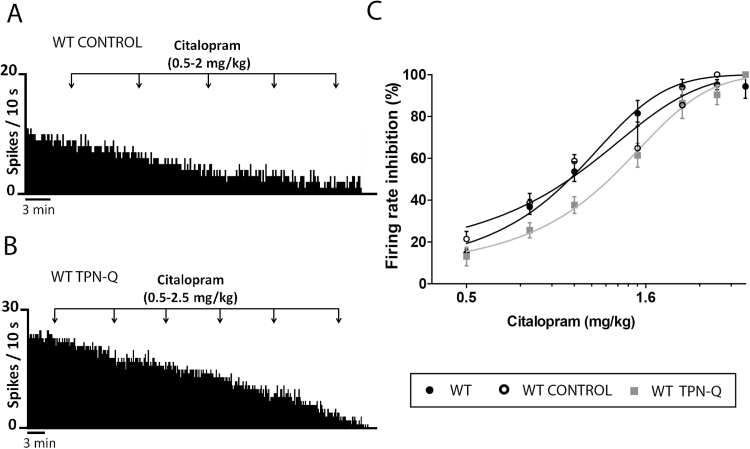
Figure 3.
Inhibitory effect of citalopram on the firing rate of dorsal raphe (DR) neurons in wild-type (WT) and tertiapin-Q injected mice. (A-B) Representative firing rate histograms illustrate the inhibitory effect of citalopram (0.5–2.5mg/kg, i.p.) on DR basal activity in artificial cerebrospinal fluid (ACSF)-injected mice (WT control, i.c.v.) (A) and tertiapin-Q injected mice (WT TPN-Q, 100 pmol, i.c.v.) (B). (C) Dose-response curves for citalopram (0.5–3mg/kg, i.p.) on DR firing rate in WT, WT control, and WT TPN-Q. Each point represents the mean±SEM of n experiments (n=4–5 mice/group).