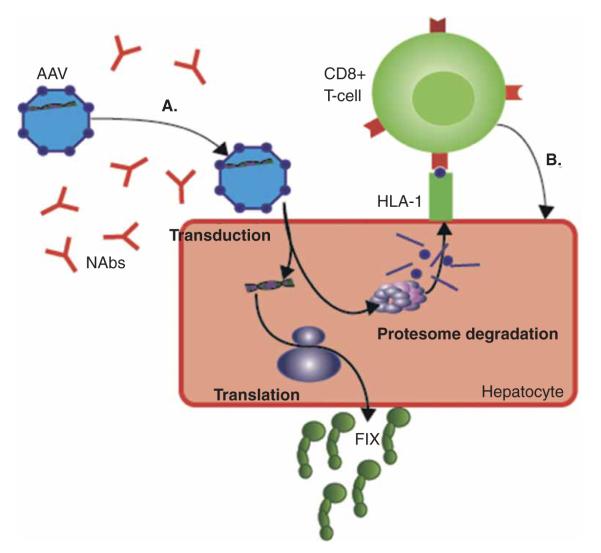
Figure 1. Current obstacles posed by the immune system for liver-directed gene therapy for hemophilia.
(A) NAb titers greater than 1:5 prevent meaningful transduction of AAV vectors. Strategies to circumvent NAbs are discussed in Section 2.1. At higher vector doses, there is a T-cell response toward the AAV capsid proteins (purple spheres) (B), which, if untreated, attenuates factor expression due to destruction of transduced hepatocytes. As discussed in Section 2.2, one strategy to overcome this cellular immune response is to improve the efficiency of transduction, translation, and the activity of FIX. Figure components are individually scaled for clarity.
AAV: Adeno-associated viral; FIX: Factor; Nabs: Neutralizing antibodies.