Figure 5.
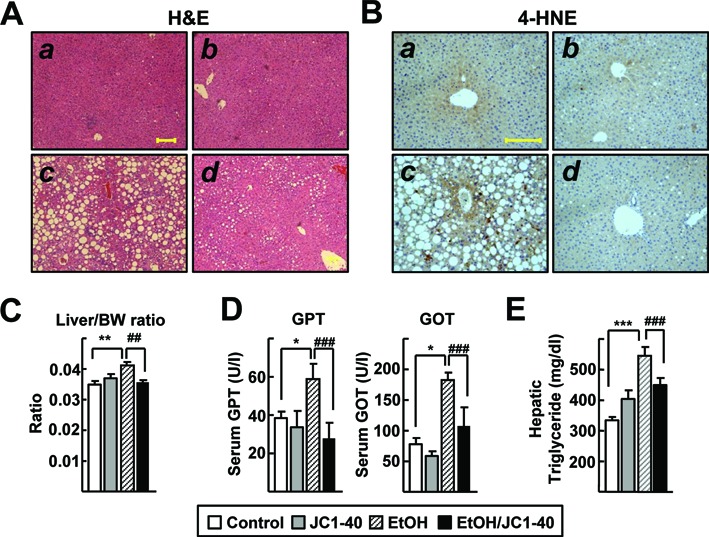
JC1–40 protects against ethanol-induced oxidative liver damage in mice. Eight week-old C57BL/6N mice were fed with the isocaloric pair-fed diet (A and B) or 5% ethanol-containing Lieber-DeCarli liquid diet (C and D) for 5 weeks. After 3 weeks of diet feeding, vehicle (A and C) or JC1–40, 10 mg/kg/day (B and D), was administered daily at doses by oral gavage for 2 weeks. (A) H&E staining of liver sections. Magnification of X100. Yellow bar represents 200 μm. (B) Immunohistochemistry staining of 4-HNE in liver sections. Magnification of X200. Yellow bar represents 200 μm. (C) Liver/body weight ratio was measured at the end of experiments. (D) Serum GPT and GOT enzyme activities were analyzed at the end of experiments. (E) Hepatic triglyceride levels were analyzed at the end of experiment. The data represent mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 versus pair-fed control group (n = 8); #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 and ###P < 0.001 versus ethanol-fed with vehicle group (n = 12).
