Figure 4.
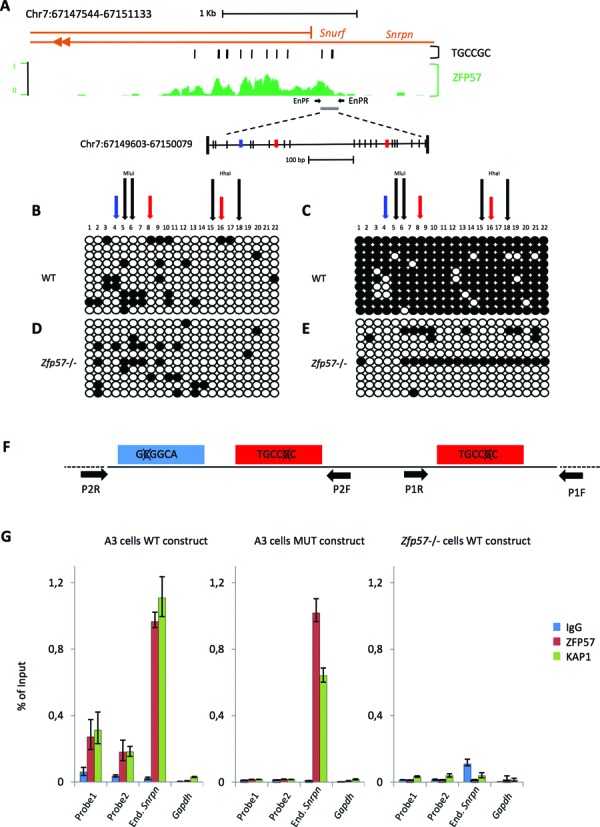
DNA methylation and ZFP57 binding at the 477 bp Snrpn/Snurf ICR transgene in WT and Zfp57 -/- ESCs. (A) Screenshot of the UCSC genome browser showing the genomic profile of ZFP57 binding in JB1 ESCs relative to the Snrpn/Snurf ICR. The location of TGCCGC motifs and 477 bp fragment used for transgenic analysis is indicated. CpGs are indicated as vertical bars. TGCCGC motif sequences present in the forward strand are in red, those present in the reverse strand are in blue. The primers (EnPF and EnPR) used for the locus-specific ChIP analysis (G) of the endogenous Snrpn locus are indicated by horizontal arrows. (B–E) DNA methylation analysis by bisulfite sequencing of individual clones of the Snrpn/Snurf ICR transgene integrated in non-methylated (B, D) or methylated (C, E) form into WT (B, C) or Zfp57 -/- (D, E) ESCs. Methylated and unmethylated CpG dinuclotides are represented as open and filled circles, respectively. Black vertical arrows indicate the positions of HhaI and MluI restriction sites used for COBRA (Figure 5A). Red and blue vertical arrows indicate the positions of the motifs on the forward and reverse strand, respectively. One representative ESC clone for each transfection is shown. (F) Diagrammatic representation of the TGCCGC motif mutagenesis in the 477 bp ICR transgene. The primers (P1F/P1R and P2F/P2R) used for the ChIP analysis of the 477 bp transgenes (G) are shown as horizontal arrows. (G) ZFP57 and KAP1 enrichment on the transgenic WT or T-mut fragments after introduction into WT or Zfp57 -/- ESCs, as determined by ChIP. Two regions (probe 1 and probe 2) of the 477 bp transgenes were analysed, by using the primers P1F/P1R and P2F/P2R, respectively. The endogenous Snrpn/Snurf ICR and Gapdh were analysed as positive and negative controls, respectively. The results are reported as percentage of input.
