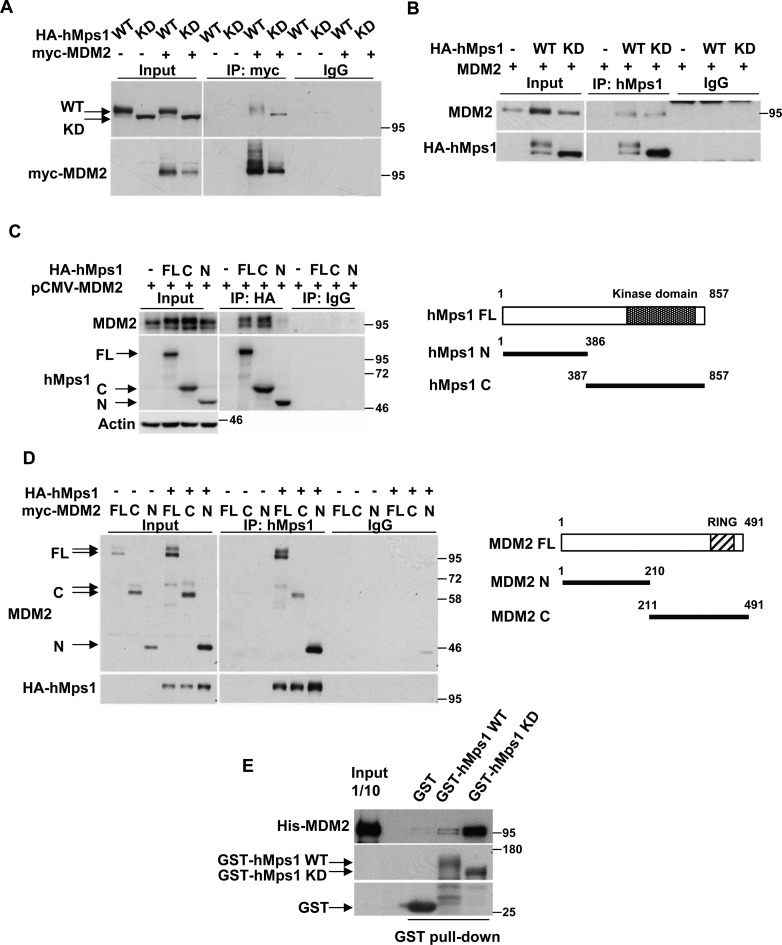
Figure 1.
hMps1 interacts with MDM2. (A and B) MDM2 interacts with hMps1 in cells. 293T cells were transfected with MDM2 together with either wild-type (WT) or kinase-dead (KD) hMps1 and cell lysates were collected and analyzed by immunoprecipitation (IP) using the anti-myc antibody (A) or the anti-hMps1 antibody (B). Anti-His antibody was used as IgG control. (C) MDM2 binds the C-terminal domain of hMps1. 293T cells were transfected as in (A) but with the full-length (FL), the N- (amino acids 1–386) or the C-terminal (amino acids 387–857) domain of HA-hMps1. Immunoprecipitation was performed using anti-HA antibody. (D) hMps1-interacting domains in MDM2. 293T cells were transfected as in (A) but with FL, the N- (amino acids 1–210) or the C-terminal (amino acids 211–491) domain of myc-MDM2. (E) Direct interaction of MDM2 with hMps1 in vitro. GST pulldown assays were performed with His-tagged recombinant FL MDM2 and the recombinant GST-hMps1 WT or KD. Results were analyzed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies.