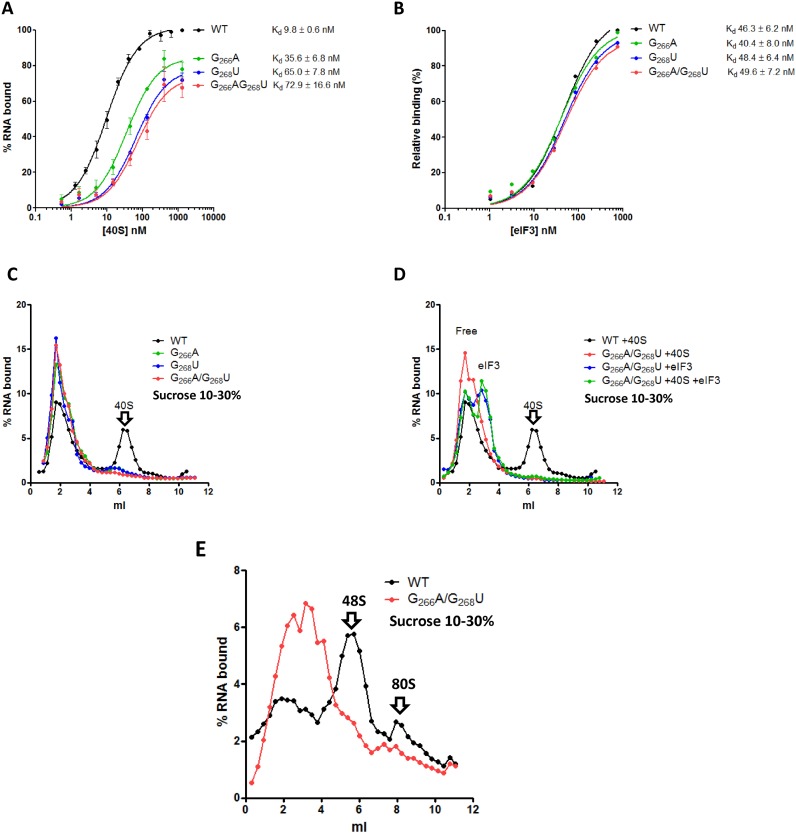
Figure 4.
Loop IIId mutants interaction with ribosomal 40S and eIF3 and pre-initiation complex assembly. Binding curves of 32P labeled WT (black) or G266A (blue) or G268U (green) or DM (G266A/G268U, red) RNAs to purified 40S ribosomal subunits (A) or to purified eIF3 (B). The results are the mean of at least three independent experiments ± standard deviation. (C) Fractionation by 10–30% sucrose density gradient on which were run 20 nM of 32P labeled WT (black) or G266A (blue) or G268U (green) or DM (G266A/G268U, red) RNAs in the presence of 400 nM of purified 40S subunits. (D) Fractionation by 10–30% sucrose density gradient of 20 nM of 32P labeled WT in the presence of excess purified ribosomal 40S (400 nM) (black) or DM RNA (G266A/G268) in the presence of excess purified ribosomal 40S (400 nM) (red), or an excess of purified eIF3 (200 nM) (blue) or both (green). (E) pre-initiation complex assembly in RRL. 32P labeled WT (black) or DM (G266A/G268U, red) RNAs were incubated in RRL pre -treated with GMP-PNP. Complexes were fractionated on a 10–30% density gradients. The results are representative of at least three independent experiments. Arrows indicating the 40S subunit were positioned according to UV profiles.