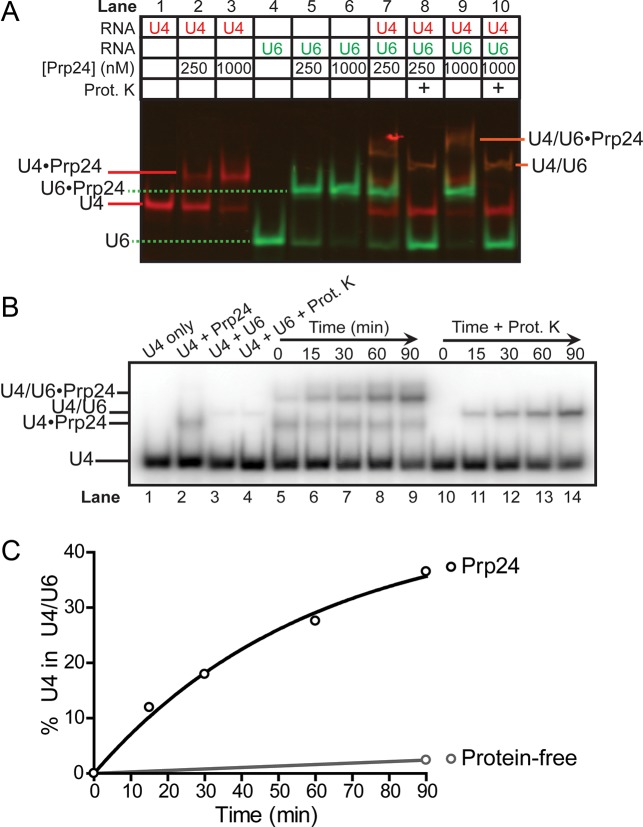
Figure 2.
Prp24 catalyzes annealing of U4 and U6 RNAs, and remains bound to product di-RNA. (A) Two-color gel demonstrating tight binding of Prp24 to Cy3-U6 (lanes 5 and 6) and weaker binding of Prp24 to Cy5-U4 (lanes 2 and 3). Co-localization of Cy3 and Cy5 fluorescence in the presence of U4 and U6 (lanes 7 and 9) shows that the slowest-migrating species (orange) contains both RNAs, and the increased mobility upon treatment with proteinase K (lanes 8 and 10) shows that the di-snRNA retains bound Prp24. Annealing reactions were incubated at 30°C for 90 min prior to loading. (B) Time-dependent formation of U4/U6, using radiolabeled U4 snRNA and unlabeled U6 and Prp24. Control reactions in lanes 1–4 were incubated for 90 min. (C) Quantification of Prp24-dependent annealing from proteinase K treated lanes (10–14) in (B) compared to protein-independent annealing (lane 4 in B).