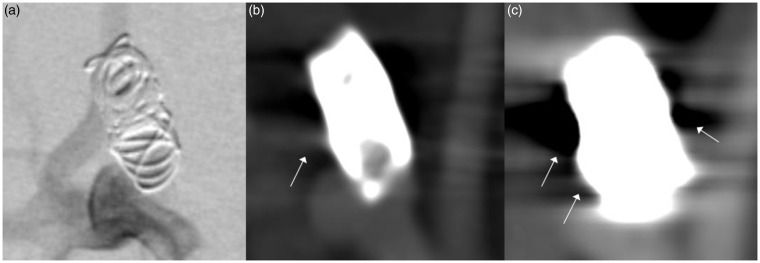
Figure 1.
Comparison of (a) digital subtracted angiography (DSA), (b) flat-detector computed tomography angiography (FD-CTA) and (c) multislice computed tomography (MS-CTA) in an aneurysm treated with coils. DSA clearly shows residual perfusion of the aneurysm neck. This could also be identified in FD-CTA, whereas in MS-CTA the aneurysm seems to be occluded completely. Beam hardening artifacts significantly impair image quality in MS-CTA, (c) (white arrows). These artifacts are also visible in FD-CTA (white arrow) but image quality is still suitable for evaluation. The size of the coil package in MC-CTA appears much larger than in DSA and FD-CTA indicating blooming artifact.