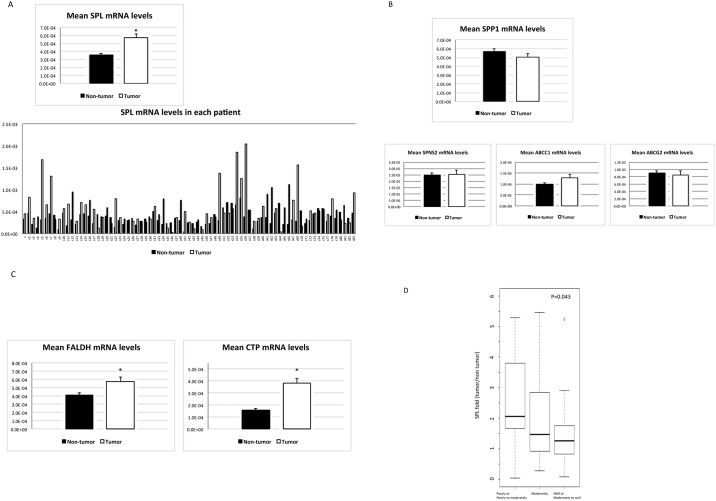
Fig 3. SPL pathway activation in HCC.
(A) As an enzyme that degrades S1P, SPL mRNA levels were elevated in HCC tissues compared with non-tumorous tissues in 70.1% of the patients; the mean SPL mRNA level was higher in HCC tissues than in non-tumorous tissues (P < 0.0001, n = 77), but SPP1 mRNA levels did not differ between HCC and non-tumorous tissues (B). In contrast, the mRNA levels of S1P transporter, SPNS2, ABCC1 and ABCG2 (B) were not altered in HCC tissues compared with non-tumorous tissues. The mRNA levels of FALDH (C), which catalyzes the formation of hexadecenoic acid from hexadecenal and CTP (C), which in turn catalyzes the formation of CDP-ethanolamine from phosphoethanolamine, were increased in HCC tissues compared with non-tumorous tissues (P = 0.011 and P <0.001, n = 77). The asterisk indicates a significant difference. (D) The mRNA expression levels of SPL in HCC tissues compared with non-tumorous tissues correlated with the degree of tumor differentiation.