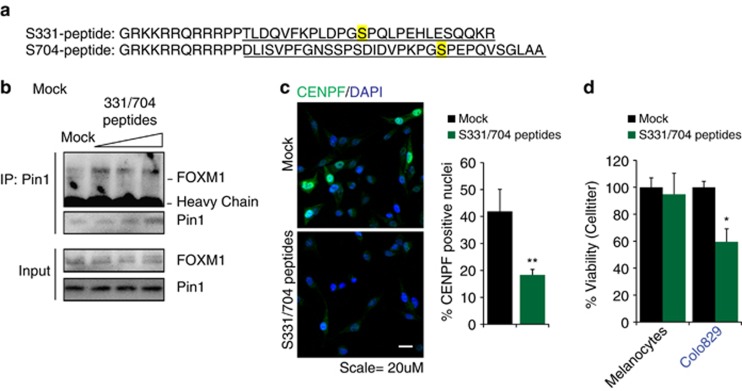
Figure 6.
Pin1-FOXM1-blocking peptides repress FOXM1 activity and BRAFV600E-driven melanoma cell survival and colony formation. (a) Sequence of the S331 and S704 Pin1-FOXM1-blocking peptides. The MEK/ERK-phosphorylatable Pin1-binding sites S331 and S704 are highlighted in yellow. The FOXM1-mimicking sequences in the peptides are underlined. The amino acids GRKKRRQRRRPP comprise the TAT sequence of HIV, used to ensure cell permeability.24 Two prolines separate the two peptide sequences. (b) A mixture of the S331 and S704 peptides represses the interaction between endogenous Pin1 and FOXM1. Colo829 cells were treated for 24 h with 5, 10 and 25 μM of each peptide in a 1:1 ratio and lysates (Input) were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) using a Pin1 antibody and immunoblot analysis using antibodies against Pin1 or FOXM1. (c) The mix of S331/704 peptides reduces CENPF expression. Colo829 cells were treated with 25 μM of each of the 331 or 704 peptides in a 1:1 ratio and CENPF immunostaining was performed. The percentage of cells with nuclear CENPF signal was quantified using Cellprofiler software. **P<0.01. (d) The mix of S331/704 peptides reduces viability of Malignant Colo829 melanoma cells, but not of neonatal Human Epidermal Melanocytes as determined via the AqueousOne Solution Cell Proliferation Assay. *P<0.05.