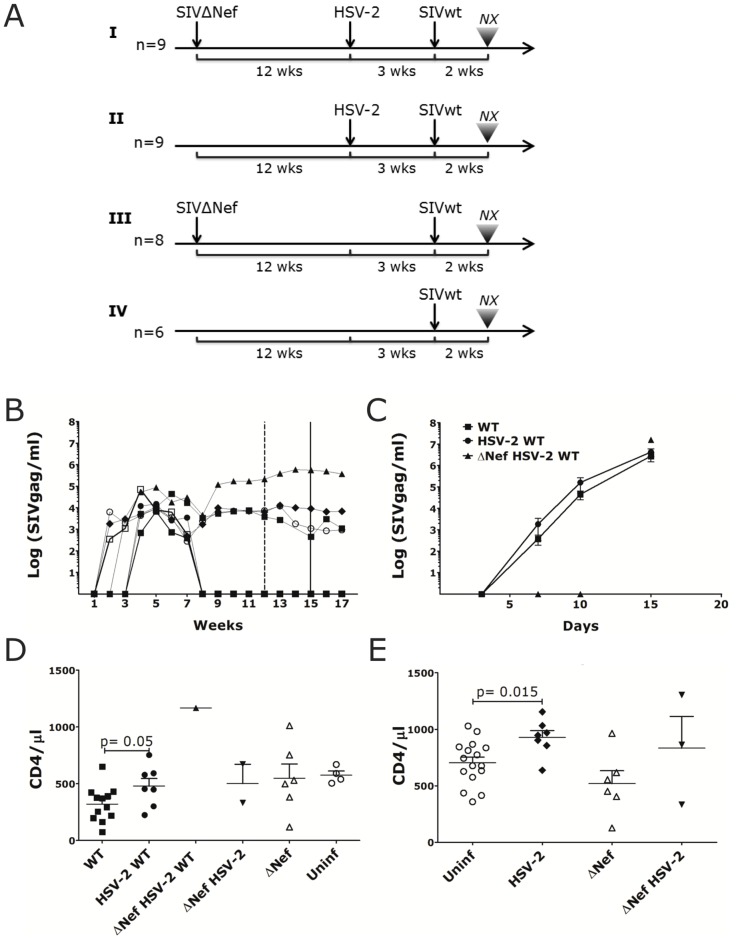
Fig 1. HSV-2/SIVmac239wt co-infected animals have higher acute plasma VL and CD4 counts.
A) Schematic representation of the rectal challenges regimen. I. n = 9 animals were inoculated with 3000 TCID50 of SIVΔNef, 12 weeks later challenged with 4x106 pfu of HSV-2 and 3 weeks later with 3000 TCID50 of SIVmac239wt. II. n = 9 animals were challenged with 4x106 pfu of HSV-2 and 3 weeks later with 3000 TCID50 of SIVmac239wt. III) n = 8 animals were inoculated with 3000 TCID50 of SIVΔNef and 15 weeks later challenged with 3000 TCID50 of SIVmac239wt. IV) 6 animals were challenged with 3000 TCID50 of SIVmac239wt as a control. The results of each infection are shown in the S1 Table. B) Plasma SIVgag RNA copies are shown for the SIVΔNef infected animals throughout the study. The dashed and full vertical lines indicate, respectively, the time of HSV-2 and SIVmac239wt challenges. C) Plasma SIVmac239wt (WT) RNA copies detected by discriminatory RT-qPCR are shown post-SIVmac239wt challenge for SIVmac239wt infected animals (WT; mean±SEM n = 12 animals at day 5 and 10, n = 5 at day 15), HSV-2/SIVmac239wt co-infected (HSV-2 WT; mean±SEM 7 animals) and for the 1 SIVΔNef/HSV-2/SIVmac239wt co-infected animal. All animals were necropsied 15 days after SIVmac239wt challenge. D-E) Blood CD4+ T cells counts 2 weeks post-WT challenge (D) and 2 weeks post-HSV-2 challenge (E) are shown for the animals that acquired HSV-2 or SIVΔNef infection compared to those that remained uninfected (Uninf). Bars represent mean ± SEM. Significant p values are shown (α<0.05).