Figure 3.
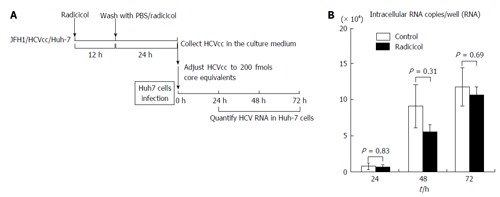
Infectivity of hepatitis C virus produced from Huh-7 cells that were treated with radicicol. A: Experimental design. To examine whether the infectivity of the JFH1/HCVcc released from the Huh-7 cells in the presence of radicicol was altered, we infected fresh Huh-7 cells with JFH1/HCVcc prepared in the presence of radicicol. To prepare a viral stock, the JFH1/HCVcc infected Huh-7 cells with 50 nmol/L radicicol were maintained for an additional 36 h. HCVcc released in the medium during the last 24 h was collected and used as the viral stock. We diluted the viral stock 59.7 times (None) and 28.6 times (Radicicol) to reduce the effects of radicicol carryover and to adjust the HCV levels (core protein level: 200 fmols). The final radicicol concentration was 1.75 nmol/L which did not affect HCV propagation. The HCV samples were added to fresh Huh-7 cells and cultured for 24, 48 and 72 h. The HCV RNA in the infected Huh-7 cells was quantified as described in the text. The multiplicities of infection for HCV were 0.2 copies/cell and 0.16 copies/cell for the HCV infection without and with radicicol, respectively; B: The copies of HCV RNA in the Huh-7 cells of each well after infection (24, 48 and 48 h) were determined as described in the text. The value of the RNA copy number in the Huh-7 cells [which were infected with the viral stock from radicicol-treated cells (values of the closed bars)] was adjusted by multiplying by a factor of 1.25. The data represent the mean values (± SE) of the results from three independent experiments. HCV: Hepatitis C virus; HCVcc: Cell culture-derived HCV.
