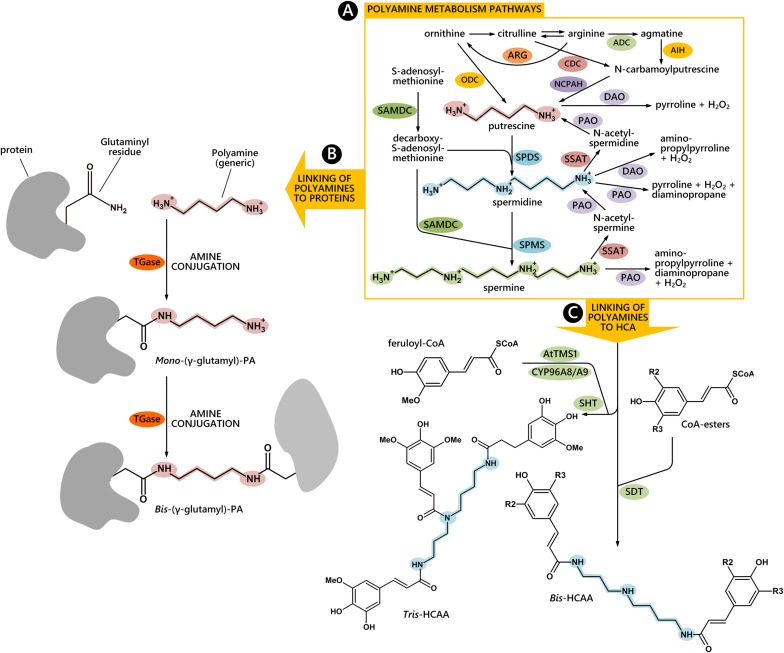
FIGURE 1.
PAs metabolism and their conjugating pathways to proteins and to hydroxyl-cinnamic acids (HCA). Free PA biosynthetic and catabolic pathways are highlighted in the yellow rectangle (A). The covalent binding to glutamyl residues of proteins gives rise to mono-γ glutamyl-PAs or to cross-links between proteins (bis-γ glutamyl-PAs) (B). The biosynthetic pathway of hydroxyl-cinnamic acids amides (HCAAs) in Arabidopsis thaliana stamens is reported according to Fellenberg et al. (2012) (C). ADC, arginine decarboxylase; ARG, arginase; AIH, agmatine iminohydrolase; CDC, citrulline decarboxylase; NCPAH, N-carbamoylputrescine amidohydrolase; ODC, ornithine decarboxylase; SAMDC, S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase; SPDS, spermidine synthase; SPMS, spermine synthase; PAO, polyamine oxidase; SSAT, spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase; DAO, diamine oxidase; TGase, transglutaminase; SHT, Spd hydroxycinnamoyl transferase; CYP98A8/CYP98A9, P450 cytochromes; AtTMS1, Arabidopsis thaliana tapetum-specific methyltransferase, SDT, spermidine disinapoyltransferase.