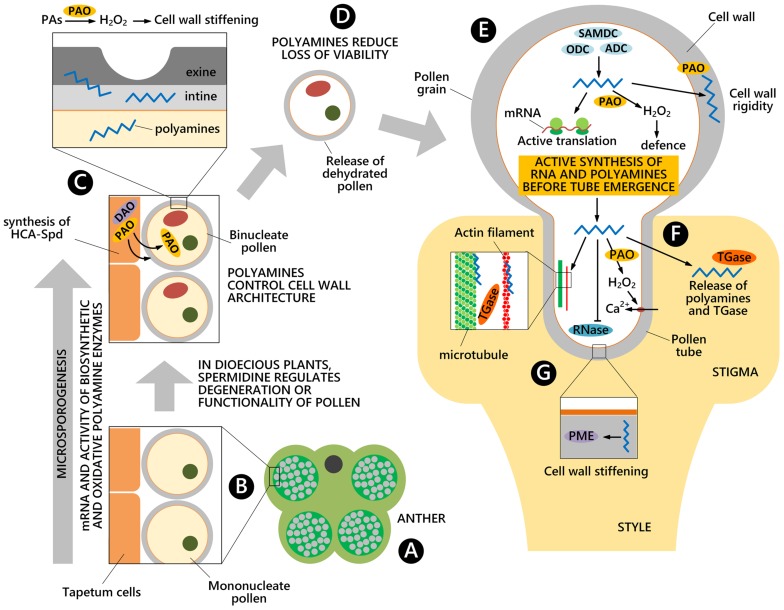
FIGURE 2.
Polyamines involvement during pollen development. PA biosynthetic and oxidative metabolisms occur from the early stage of pollen formation inside the anthers (A), when both microspores and the tapetal cell layer of the anther contribute to microspore cell wall architecture (B). Pollen accumulates high levels of free PAs and HCAAs, mainly localized in the cell wall. PA catabolism by PAO and DAO modulates the rigidity of the cell wall (C). Once dehydrated, pollen grains are released and PAs contribute to maintain pollen viability (D). During germination on a stigma (E), PAs promote the translation of transcripts and they are also released in the extracellular space, together with TGase (F). During pollen tube growth in a compatible style, PAs take part in the cytoskeleton organization, in cell wall deposition and remodeling by the PME enzyme as well as in the regulation of ion transport through the plasma membrane. PAs also exert an inhibitory effect on RNase enzymes (G).