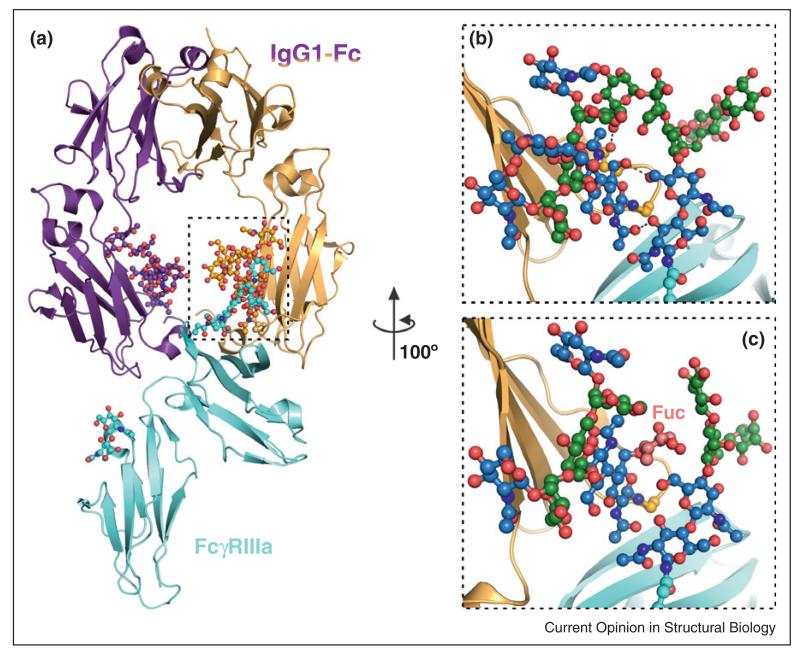
Figure 4.
The impact of N-linked glycans in modulating protein complexes. (a) Crystal structure of the glycosylated complex between the IgG1-Fc region and its FcγRIIIa receptor, essential for antibody-mediated cellular cytotoxicity [72••]. (b) Antibodies lacking core fucosylation show a large increase in affinity for FcγRIIIa, due to additional glycan–glycan and glycan–protein interactions (putative hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines). This leads to an improved receptor-mediated effector function and forms the basis for a next generation of therapeutics, glycoengineered antibodies. (c) In the complex structure containing fucosylated IgG1-Fc, such contacts are very limited, explaining the decreased affinity for the FcγRIIIa receptor. Fuc: fucose attached to the Asn297-linked GlcNAc in IgG1-Fc. Colour coding of carbon atoms in the glycan units (sphere and stick representation) in panels (b) and (c) is as described in Figure 2.