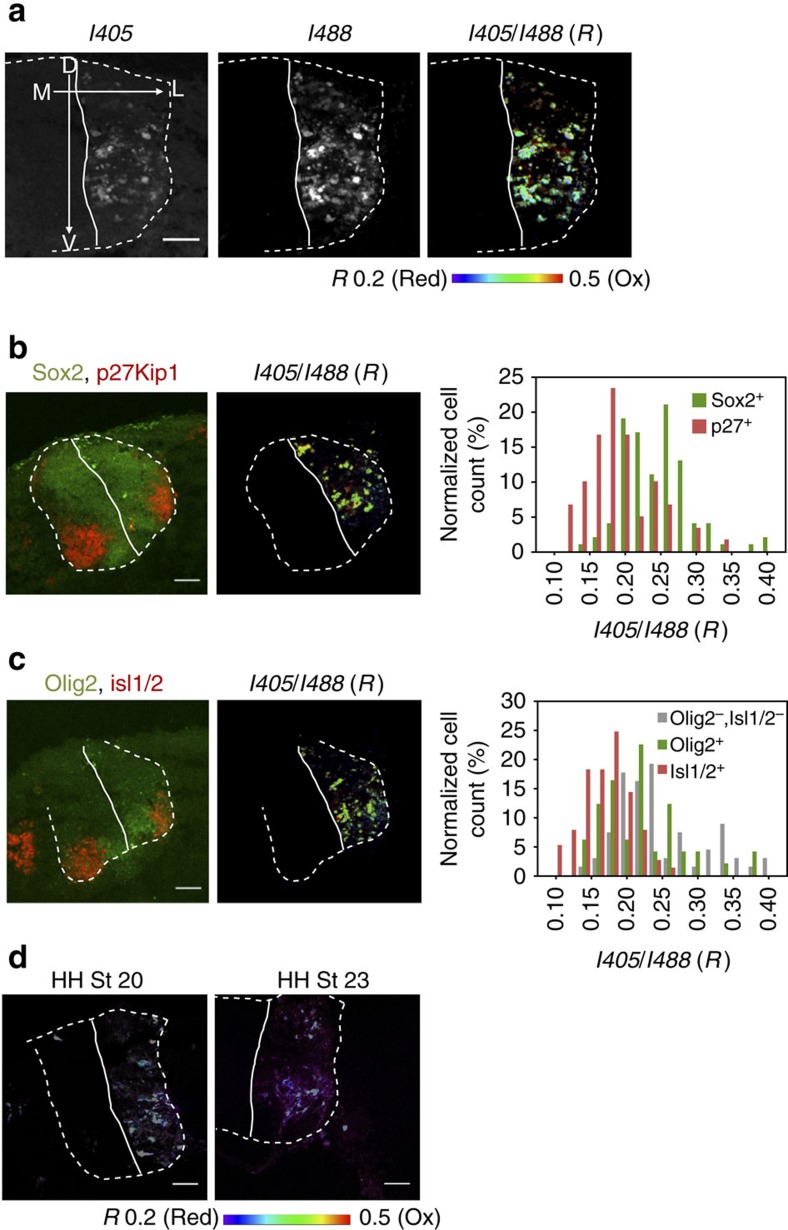
Figure 3. Redox status of cytosolic glutathione within neurons of chicken spinal cord.
(a) Representative Grx1-roGFP2 image illustrates variation of redox states in neuronal cell population within a spinal cord. The R values (0.20–0.50) are shown with the pseudo-colour scale that corresponds to 0 to 29% oxidation of the sensor. Scale bars, 50 μm. (b) Distribution of R values in different cell populations. The sections were stained for Sox2 and p27Kip1 which define the regions of actively cycling cells (Sox2+) and differentiated cells (p27Kip1). Scale bar, 50 μm. (higher magnification is shown in Supplementary Fig. 9a). The ratio I405/I488 (R value) for Sox2+ (0.24±0.06; n=102) is significantly higher than in p27Kip1+ (0.18±0.05, n=60) regions (Student's t-test, P<0.001). (c) The sections were stained for Olig2 and Isl1/2 which define cycling motor neuron progenitors and postmitotic motor neurons, respectively. Scale bar, 50 μm. The R values for Olig2−:Isl1/2− (0.25±0.07; n=68), Olig2+:Isl1/2−(0.23±0.09, n=49) and Olig2−:Isl1/2+ (0.16±0.03, n=77) regions. See Supplementary Fig. 9b for magnified view. Differences between Olig2−/Isl1/2+ from other regions are significant at P<0.001. There is no statistically significant difference between Olig2−:Isl1/2− and Olig2+:Isl1/2− regions (P=0.06). (d) Cytosolic glutathione in neuronal cells is more reduced in embryos at the later development stage. Embryos at HH stage 23 were compared with the stage 20 embryos (see Supplementary Fig. 8b and c for full information). Scale bar, 50 μm.