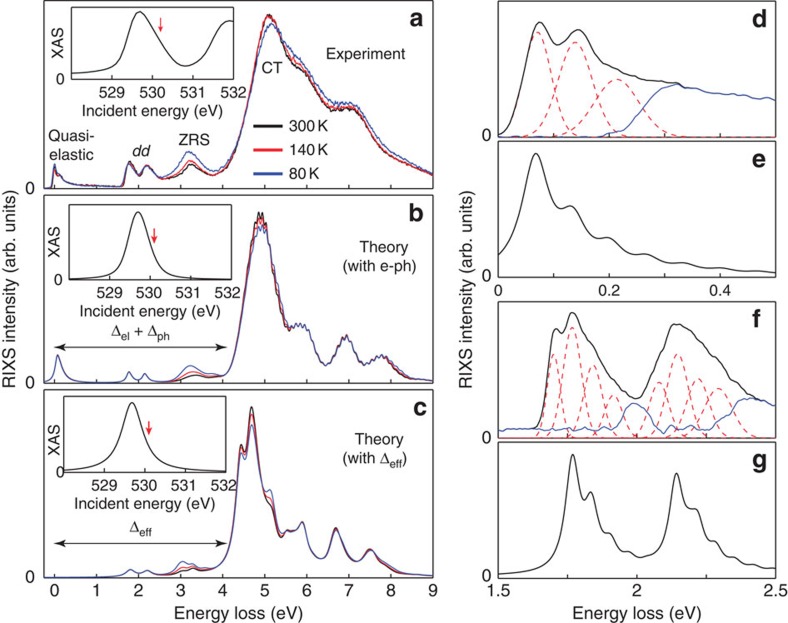
Figure 2. XAS and RIXS spectra of LCO at the oxygen K-edge.
(a) The measured RIXS spectra, recorded at various temperatures, as indicated. The incident photon energy for these measurements was detuned slightly from the upper Hubbard band peak in the XAS, as shown in the inset. The incident phonon energy is indicated by the red arrow. (b) The calculated RIXS spectra obtained using a cluster model that includes coupling to the O–O bond-stretching mode. The calculated XAS spectrum is shown in the inset. For comparison, c shows calculated spectra obtained from a model without coupling to the phonon mode and with an increased value of 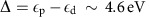 . The detailed measured RIXS spectra highlighting the harmonic phonon excitations in the quasi-elastic and dd-excitation energy loss range are shown in d and f, respectively. Here, the red dashed lines show Gaussian fits to these data that highlight the individual phonon excitations. The blue line is the difference between the data and the red dashed lines. The corresponding RIXS calculations are shown in e and g, respectively. In d–g the incident photon energy coincides with the peak in the XAS intensity. Note that the elastic line has been removed from all of the calculated RIXS spectra for clarity. The spectra in e and g have been broadened using a Gaussian line shape with a s.d. of 60 meV. In b and c this width was increased to 130 meV to mimic additional broadening of CT features due to the bands formed by the O 2p orbitals that are not well captured by our small Cu3O8 cluster calculation.
. The detailed measured RIXS spectra highlighting the harmonic phonon excitations in the quasi-elastic and dd-excitation energy loss range are shown in d and f, respectively. Here, the red dashed lines show Gaussian fits to these data that highlight the individual phonon excitations. The blue line is the difference between the data and the red dashed lines. The corresponding RIXS calculations are shown in e and g, respectively. In d–g the incident photon energy coincides with the peak in the XAS intensity. Note that the elastic line has been removed from all of the calculated RIXS spectra for clarity. The spectra in e and g have been broadened using a Gaussian line shape with a s.d. of 60 meV. In b and c this width was increased to 130 meV to mimic additional broadening of CT features due to the bands formed by the O 2p orbitals that are not well captured by our small Cu3O8 cluster calculation.