Figure 1.
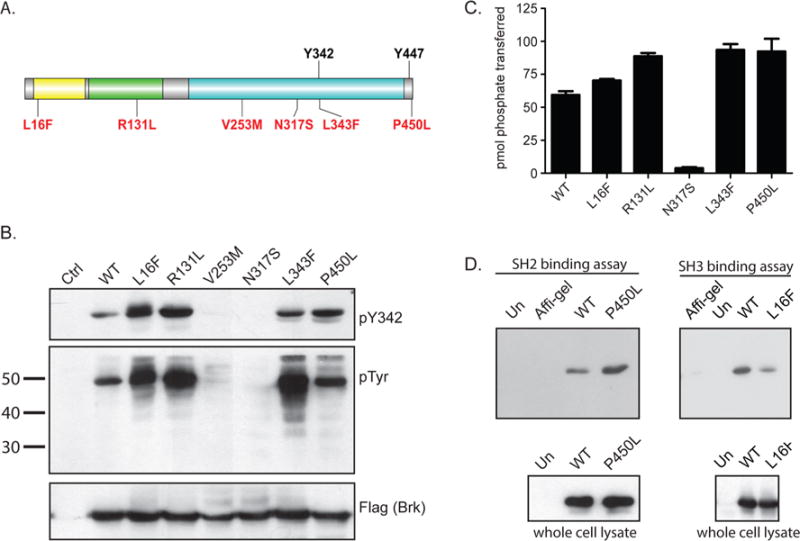
Cancer-associated mutations affect Brk activation and intramolecular interactions. (A) The domain arrangement of Brk is shown schematically. The autophosphorylation site (Tyr 342) and inhibitory tyrosine (Tyr 447) are in black. The cancer-associated mutations are indicated in red. (B) Lysates from 293T cells expressing Flag-tagged wild-type or mutant forms of Brk were probed with anti-phosphoBrk (pY342), phosphotyrosine, and Flag antibodies. The gel is representative of five similar experiments. (C) Wild-type and mutant forms Brk were immunoprecipitated from transfected 293T cells using anti-Flag M2 affinity gel, then incubated with Src-substrate peptide in the presence of [γ32-P] ATP. The activities were measured in duplicate with the phosphocellulose paper assay. The results are representative of three experiments. The error bars show standard deviations. (D) Lysates from Src−Yes−Fyn− null (SYF) cells expressing wild-type or mutant forms of Brk were incubated with SH2 ligand (left) or SH3 ligand (right) conjugated to agarose beads. Bound protein was eluted with SDS-PAGE sample buffer and resolved by SDS-PAGE, then probed with anti-Brk (left) and anti-Flag (right) antibodies. Affi-gel control samples contained lysates from wild-type Brk expressing cells incubated with nonconjugated beads. Untransfected controls (Un) contained untransfected cell lysates with peptide conjugated beads.
