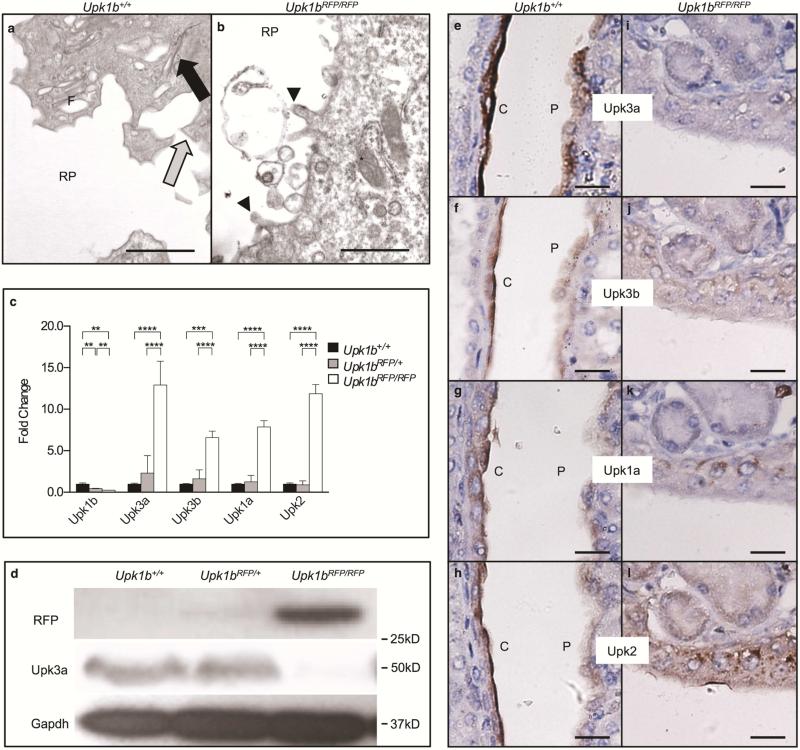
Figure 5. RFP-disrupted Upk1b Leads to Defective Urothelial Plaque in the Kidneys.
(A, B) Ultrastructural analysis of the apical surface of the cortical, renal urothelial superficial cell layer in Upk1b+/+ and Upk1bRFP/RFP kidneys was assessed by transmission electron microscopy. RP: Renal Pelvis, Black Arrow: Parallel membranes, Gray Arrow: Pointed Apical Projections, Arrowhead: Blunted Apical Projections, F: Fusiform Vesicles. Asterisk: Mitochondria. (C) Uroplakin mRNA expression in Upk1b+/+, Upk1bRFP/+ and Upk1bRFP/RFP kidneys was evaluated by qPCR (n=3 Upk1b, n=6 Upk3a, Upk3b, Upk1a, Upk2). Raw data was normalized to Gapdh and fold change relative to Upk1b+/+ is graphed. A Two-Way ANOVA and Tukey's multiple comparison post-hoc test were used to evaluate statistical significance. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001., ****p < 0.0001. Error bars represent standard error. (D) Protein expression in Upk1b+/+, Upk1bRFP/+ and Upk1bRFP/RFP kidneys was evaluated by immunoblotting for the antibodies indicated. (E-L) Renal urothelial morphology in Upk1b+/+ and Upk1bRFP/RFP kidneys was evaluated by immunohistochemistry for the antibodies indicated. Scale bar indicates 1μm (A, B), 25μm (E-L).