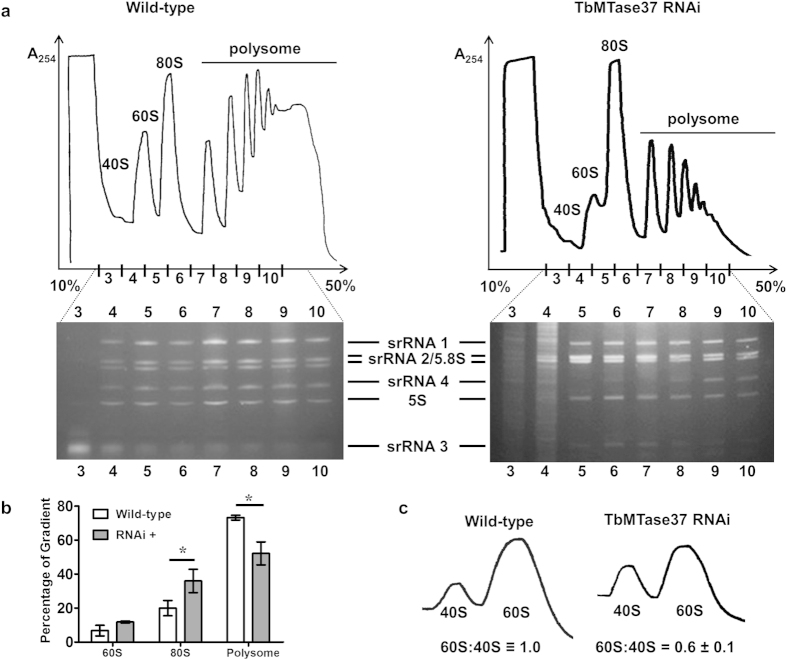
Figure 5. Down-regulation of TbMTase37 leads to reduction in Polysome-associated ribosomes and 60S subunit levels.
(a) T. brucei lysates from wild type and RNAi cells were separated by sucrose gradient centrifugation (10–50% sucrose is shown) and fractions monitored by A254. Peaks corresponding to 40S, 60S, 80S and polysome-associated ribosome are as indicated. Lanes correspond to the fraction number indicated and the identity of the 6 small rRNA bands in the gel are as indicated. Gradients and gels were loaded with equal A260 units. (b) The area under polysome traces was quantified for wild-type and MTase37 RNAi polysomes experiments. Quantification was performed using the Measure feature of ImageJ (NIH). A baseline was first drawn across the bottom of polysome traces and then peaks were extrapolated down to the baseline. The area under the trace for 60S, 80S and polysome associated ribosomes was calculated and graphed as a percentage of the total area. Analysis was performed on 3 independent traces and significance (p-value < 0.05) was determined using a two-tailed t-test and is denoted by an asterisk. (c) Ribosomes from wild type and induced TbMTase37 RNAi cells were dissociated into free subunits in the absence of Mg2+ and separated through 7–27% sucrose gradients. To quantify percent reduction of 60S subunits after RNAi, the ratio of 60S to 40S was set to 1. The 60S:40S ratio for RNAi is the percent reduction compared to wild type. Error represents standard deviation of three independent replicates.