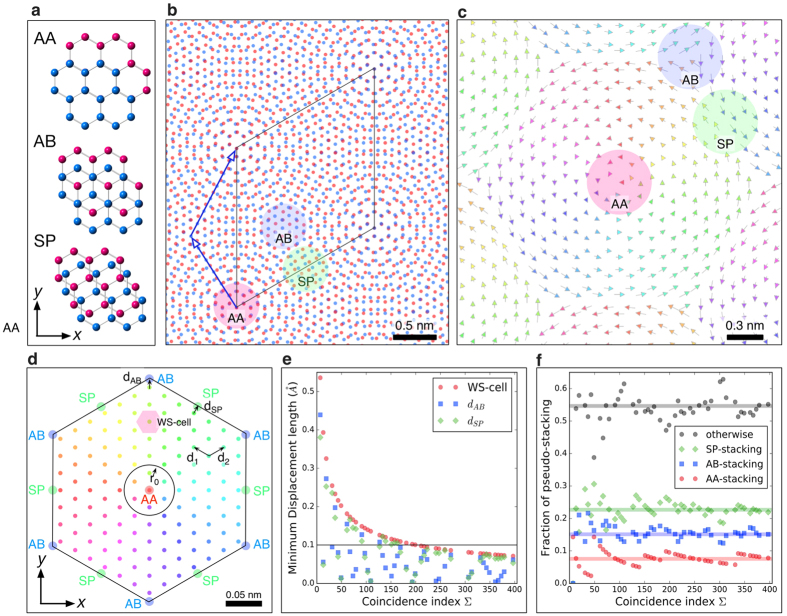
Figure 3. DSC vector map and DSC lattice of ∑127 twisted graphene.
(a) The structure models of AA-, AB- and SP-stacking-order (blue and red atoms are the respective layers). The translation vector from AA- to AB- or SP-stacking-order is (a1 + a2)/3 or a1/2, respectively. The direction of x- and y-axis are a1 + a2 and a1 − a2, respectively. (b) The structure model of TBG ∑(6,7) = 127 with AA-stacking. The blue arrows on the blue-layer show the moiré lattice vector of τ1 (=6a1 + 7a2). The overlaid red, blue and green circles are located on pseudo AA-, AB- and SP-stacking areas, respectively. The blue and red layers are rotated +θ/2 or −θ/2 from y-axis, respectively (θ = 5.09°). (c) DCS vectors from red- to blue-lattices in the same coordination of (a), where the arrow colors correspond to direction. (d) DSC lattice map for TBG ∑(6,7) = 127 in the same coordination of (a), where the origin is denoted by AA. The color of DSC lattice indicates the direction of DSC vector as in (c). The notation of AB (blue color) and SP (green color) in the large cell indicate the positions of AB and SP stacking order. d1, d2 are the DSC basic vectors and the WS-cell of the DSC lattice is shown by the small red hexagon, r0 is defined to be the area containing translation vectors belonging to a specific pseudo-stacking order. (e) Minimum displacement shift for AB- and SP-stacking with κ = 0 as a function of coincidence index. (f) Fraction of pseudo AA-, AB-, SP- and other-stacking orders as a function of coincidence index, where the horizontal colored lines are the estimated fractions with the criterion of r0 = a0/4 (0.20 Å).