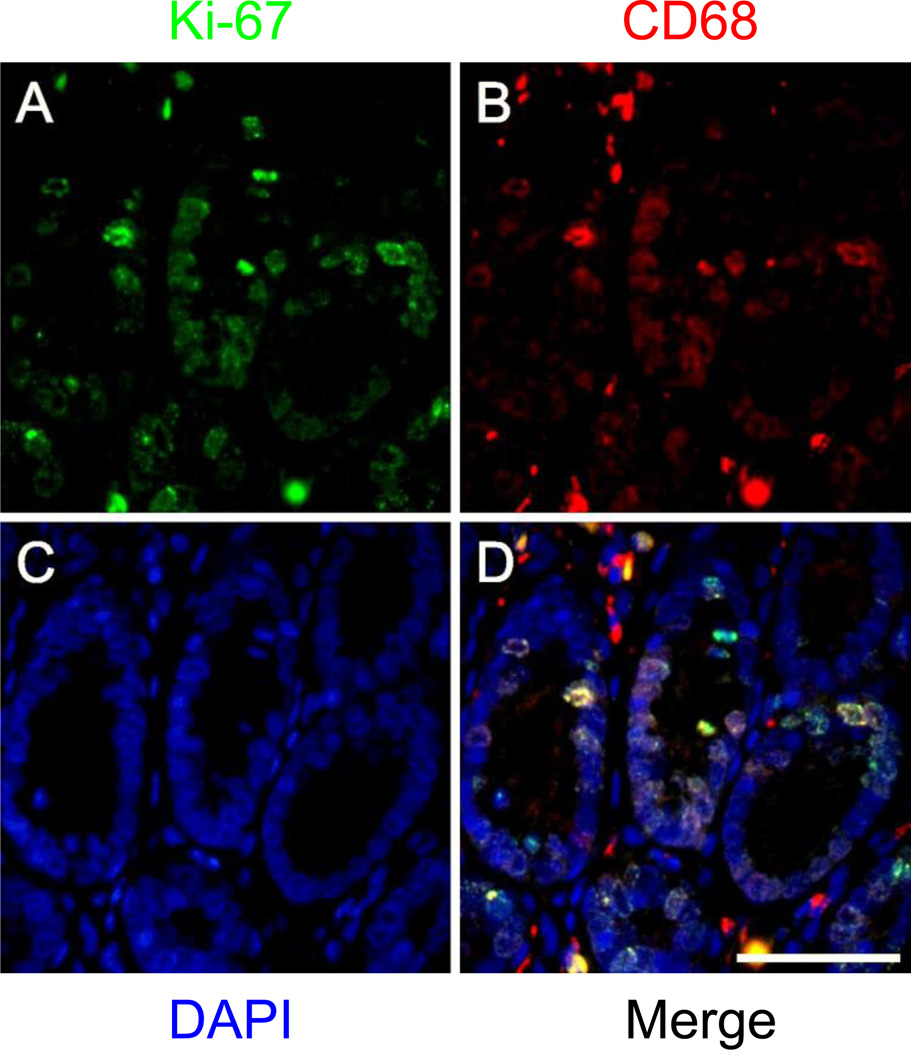
Fig. 5.
Artifactual co-localization resulting from interaction between tissue-bound anti-mouse secondary antibody and biotinylated CD68 antibody in formalin-fixed paraffin embedded colon from a normal rat. Images depict crypts and lamina propria in normal colonic mucosa. Staining for Ki-67 (unconjugated primary antibody, green), CD68 (biotinylated primary antibody, red), and DAPI (blue) as well as an overlay of the green, red, and blue channels are shown in a–d, respectively. Nuclear CD68 staining in b coincides with Ki-67-positivity in crypt nuclei in a and indicates artifactual co-localization, which results when free binding sites on tissue bound anti-mouse secondary antibody are not saturated with isotype mouse IgG1. Scale bar = 50µm