Figure 2.
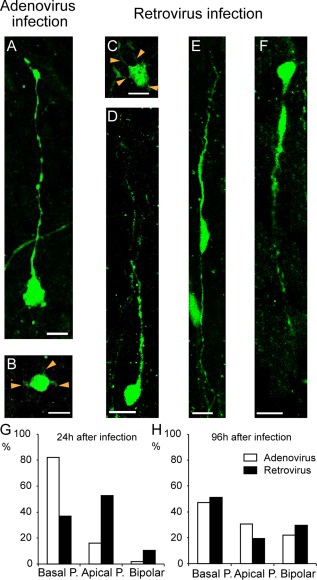
Examples of the different morphotypes of OSVZ EGFP+ precursors on organotypic slices immunostained for EGFP after 1 day in vitro following EGFP adenoviral infection (A,B) or EGFP retroviral infection (C–F) at E76. Following adenoviral infection, two main types of precursors were observed: (A) bRG with only a basal process, referred to as bRG‐basal‐P and (B) multipolar cell with thin processes (orange arrowheads). Following retroviral infection, four different precursor types were observed: (C) multipolar cell with processes (orange arrowheads), (D) bRG‐basal‐P, (E) bRG bearing both an apical and a basal process referred to as bRG‐both‐P (note that the two processes have different thickness and they extend through the OSVZ depth, and (F) bRG cells bearing a well‐developed apical process referred to as bRG‐apical‐P. G: Proportions of morphologies observed 24 hours following infection. Adenoviral infection results in GFP being selectively expressed in bRG‐basal‐P (>80%) (n = 132). By contrast, GFP is expressed in all three stable morphotypes after retroviral infection. H: 96 hours after adenoviral or retroviral infection, similar frequencies of bRG‐basal‐P, bRG‐apical‐P, and bRG‐both‐P are observed (n = 96). Scale bar = 10 μm in A–F.
