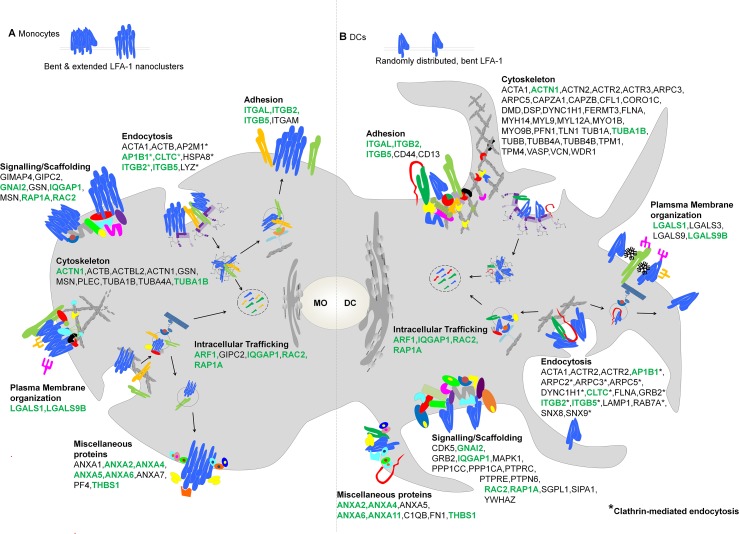
Fig 7. Model for the Spatio-Functional Regulation of LFA-1 in monocytes and DCs.
Schematic representation of LFA-1 binding partners (described by gene symbols) in monocytes and DCs, selected from the full lists of enriched proteins identified in these cell types in this study (Table 1, S1 and S2 Tables). The authors selected the binding candidates according to their established or potentially novel role in integrin function and cell adhesion, based on the current literature. Candidates were grouped into categories according to their potential role and/ or cellular localization. In monocytes, in the absence of ligand, LFA-1 (heterodimer formed by an αL (ITGAL) and β2 (ITGB2) chain) is functionally active and forms nanoclusters consisting of extended or inactive (bent) LFA-1 molecules in the PM (A). During differentiation of monocytes towards DCs (B) LFA-1 activity is lost (all molecules are in the bent conformation) and LFA-1 shows a random PM distribution. LFA-1 binding partners identified in both monocytes and DCs are highlighted in green.