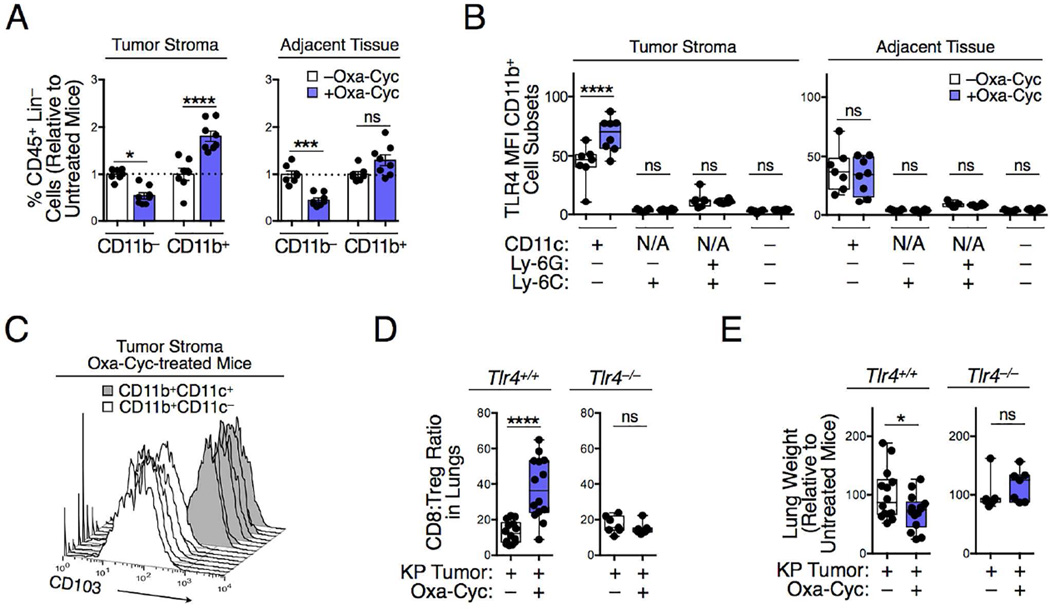
Figure 5. Drug-induced tumor control involves innate immunity and TLR4 signaling.
A) CD11b− and CD11b+ cells in lung tissue biopsies of KP mice that received Oxa-Cyc or were left untreated (n=7-8 mice per group). Lung tissue biopsies of tumor and tumor-free adjacent tissues were investigated in parallel. (B) TLR4 mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of CD11b+ cell subsets in tumor and tumor-free lung tissues of Oxa-Cyc treated or untreated KP mice (n=7-8 mice per group). (C) CD103 phenotype of CD11b+CD11c− and CD11b+CD11c+ cells in tumor stroma of Oxa-Cyc-treated mice (n=7 mice per group). (D and E) Lung CD8+ T cell:Treg cell ratio (D) and lung weight (E) of KP1.9 tumor-bearing Tlr4+/+ and Tlr4−/− mice treated or not with Oxa-Cyc (n=7-14 mice per group). Lineage (Lin) defined as (B220/CD49b/CD90.2/Ter119)+. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; ns, not significant; N/A, not applicable.