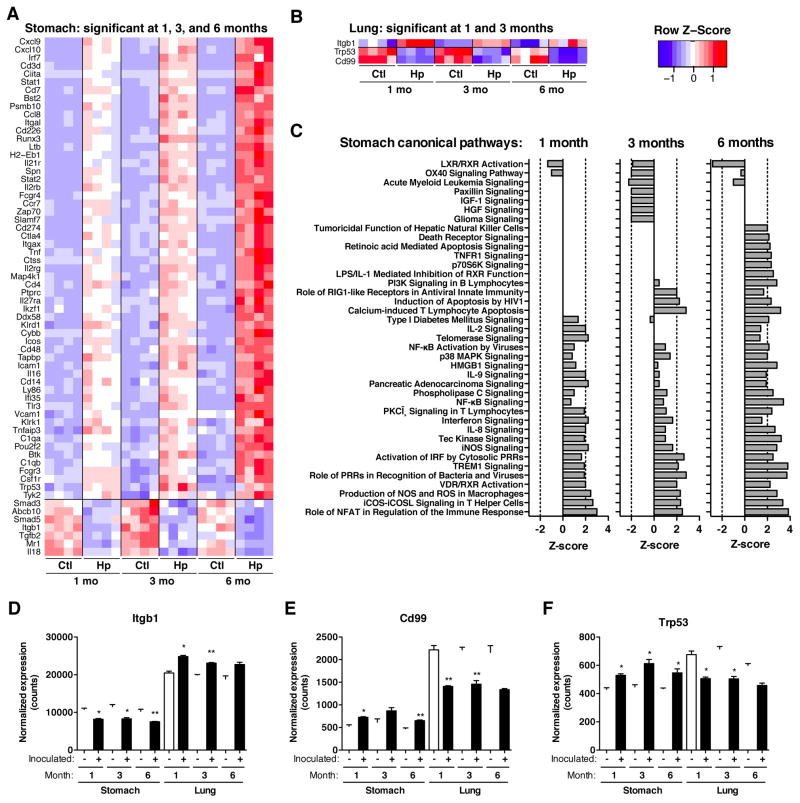
Figure 3. Immunologic genes consistently altered by gastric H. pylori infection in stomach and lung.
Immunologic gene expression was measured by hybridization using Nanostring (nCounter) technology in (A) gastric and (B) pulmonary tissues at 1, 3, and 6 months after colonization in Cohort 1 mice. Heat maps show expression levels of genes significantly different (FDR-adjusted p-value <0.05, t-test) at all three time points for the stomach and at 2 time points for the lung. (C) Gastric canonical pathways, significantly induced or repressed by H. pylori-infection. (D–F) Relative expression levels (normalized counts) for genes significantly different in ≥ 2 time points in each tissue. False-discovery rate adjusted p-values: *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, t-test. See also Figure S3.