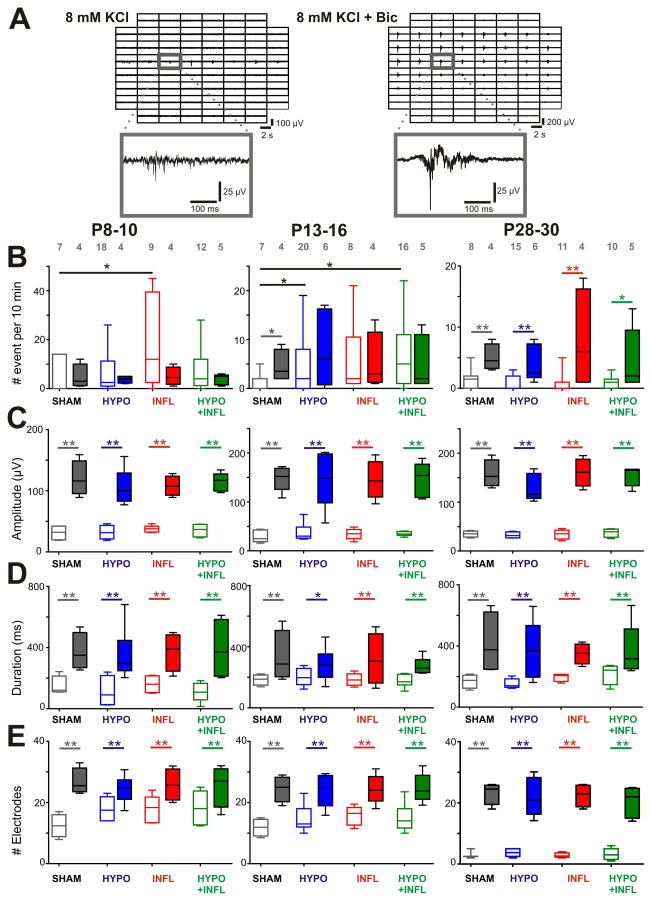
Figure 4. Bicuculline increase EEs frequency and amplitude in all conditions.
Examples of EEs recorded from a slice prepared from a P8–10 HYPO animal in ACSF containing 8 mM KCl alone or together with bicuculline. For both recording solutions, 500 ms recording traces show the activity recorded by each of the 60 electrodes of the MEA during a spontaneous EE. The recording trace on the electrode marked by a grey square is magnified below. Note the larger spreading of the events with bicuculline, as well as the longer duration and higher amplitude. B) The mean frequencies of EEs occurrence in a ten minute recording period per slice and per condition is plotted as box and whisker plots (SHAM, dark grey; HYPO, blue; INFL, red; HYPO+INFL, green). For each age group, the mean number of occurrence is plotted for 8 mM KCl ACSF (open boxes), and 8 mM KCL-ACSF + Bic (filled boxes). C) Increase of the amplitude, D) duration, and E) number of electrodes with synchronous activity of epileptiform events in presence of Bic for each condition. Dunns test: **, p<0.01; *, p<0.05.