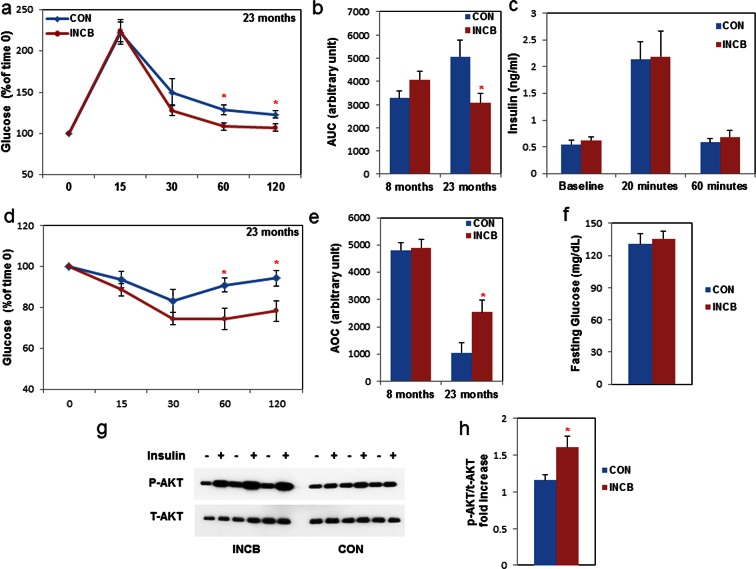
Figure 8. JAK inhibition increases insulin sensitivity in aged mice.
Seven-month old and twenty-two-month old male mice were treated with vehicle (CON) or ruxolitinib (INCB) daily. An oral glucose tolerance test was performed after 5 weeks of treatment. (a) Glucose level was monitored over 120 minutes for 22-month old mice (the results for 7-month old mice are shown in Figure 8—figure supplement 1) and (b) the area under the curve (AUC) was calculated. Results (N=6 for CON and INCB groups of 8-month-old mice, N=9 for CON and INCB groups of 22-month-old mice) are expressed as mean ± s.e.m. *p<0.05. (c) Plasma insulin was measured at baseline, 20 minutes, and 60 minutes after oral glucose gavage. Results (N=9) are expressed as mean ± s.e.m. *p<0.05. An insulin tolerance test was performed after 6 weeks of the treatment. (d) Glucose was monitored over 120 minutes for 22-month old mice (the results for 7-month old mice are shown in Figure 8—figure supplement 1) and (e) area over curve (AOC) was calculated. Results (N=9) are expressed as mean ± s.e.m. *p<0.05. (f) Fasting glucose levels (N=9) are expressed as mean ± s.e.m. *p<0.05. (g) WAT tissue was collected and cultured in CM with or without 5 nM insulin for 5 minutes at 37oC and tissue lysates were then prepared. p-AKT (Ser473) and total AKT protein abundance were assayed. Representative images are shown. (h) These signals were quantified by densitometry using ImageJ. The ratios of p-AKT/total AKT are expressed as mean ± s.e.m. N=6. *p<0.05. Two-tailed Student's t tests were used to determine statistical significance.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.12997.024
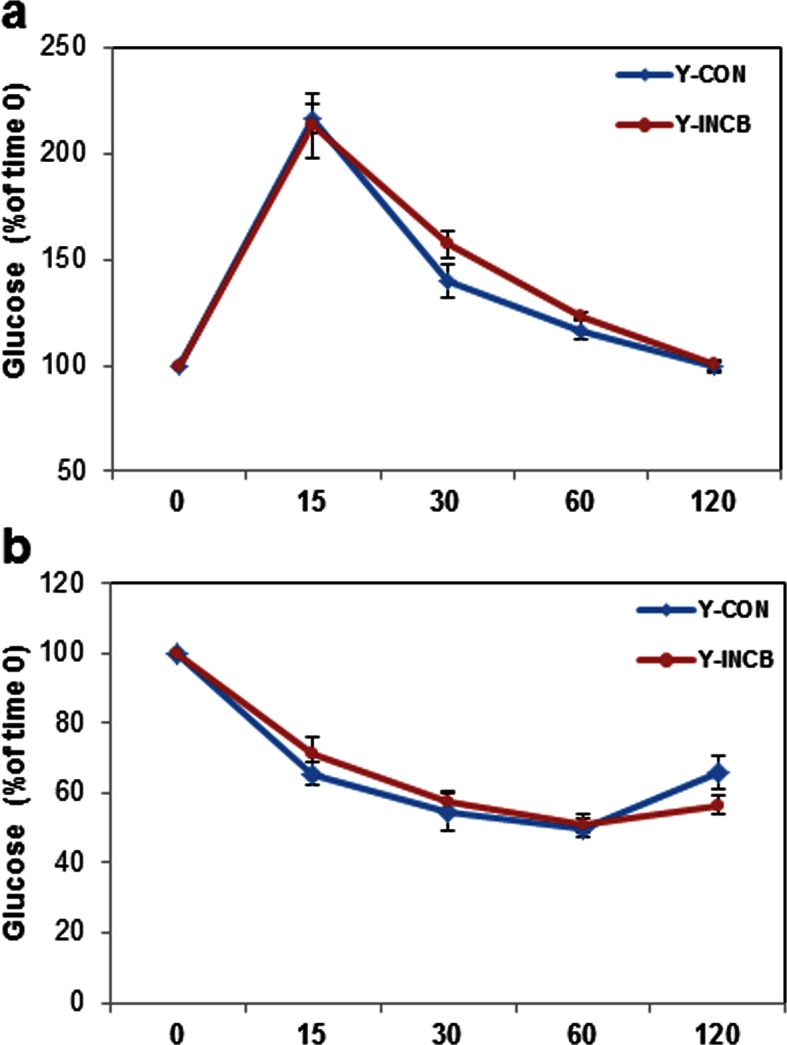
Figure 8—figure supplement 1. JAK inhibition had less impact on glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity in 8-month old mice compared to 22-month old mice.