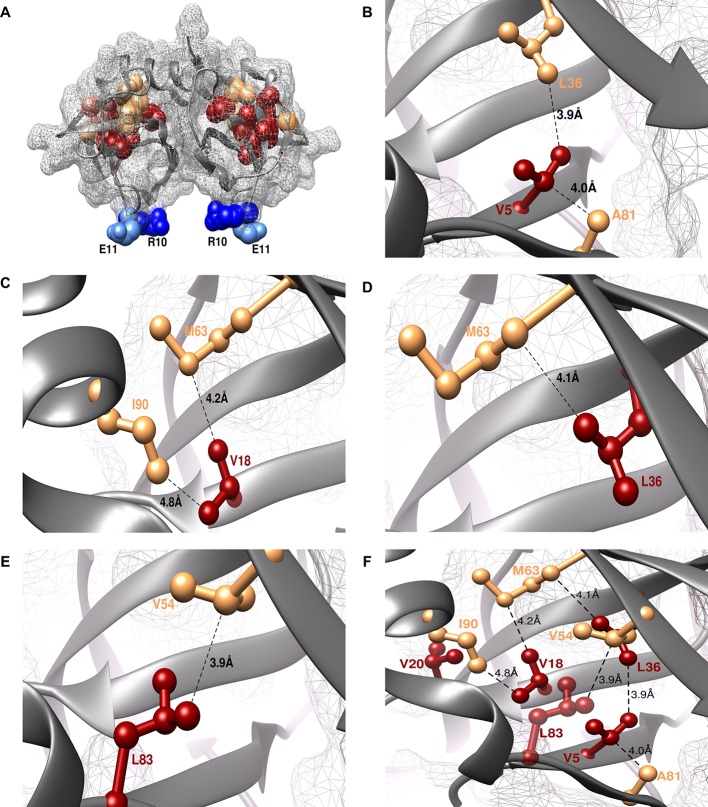
Figure 3. Experimentally obtained (Parent inactive mutant, suppressor) pairs mapped onto the crystal structure of CcdB (PDB id 3VUB [Loris et al., 1999]).
Only the Wild-Type (WT) residues of each member of the pair are shown as structures of the mutants are not available. (A) The two monomers of the dimeric CcdB protein are shown in ribbon (dark grey) with the distal suppressors (R10 (dark blue) and E11 (light blue) mapped on an exposed loop region while the proximal suppressors (light brown) and parent inactive mutants (dark red) are present in the core of the protein. One of the monomers of the dimeric CcdB protein has been shown in B-F for ease of visualization of the mapped parent inactive mutants and corresponding proximal suppressors. (B) Parent inactive mutant V5 and its proximal suppressors L36 and A81, (C) Parent inactive mutant V18 and its proximal suppressors M63 and I90, (D) Parent inactive mutant L36 and its proximal suppressor M63, (E) Parent inactive mutant L83 and its proximal suppressor V54 are shown. Dotted lines indicate the shortest distance between the two residues in each pair. (F) (Parent inactive mutant, proximal suppressor) pairs are clustered in the core of the protein forming an interconnected network, with side chains facing towards each other. Residues common to multiple (Parent inactive mutant, suppressor) pairs, for example L36 and M63, provide additional information about the network of interactions. The figure has been prepared using the UCSF Chimera package (developed by Resource for Biocomputing, Visualization, and Informatics at the University of California, San Francisco [Pettersen et al., 2004]).