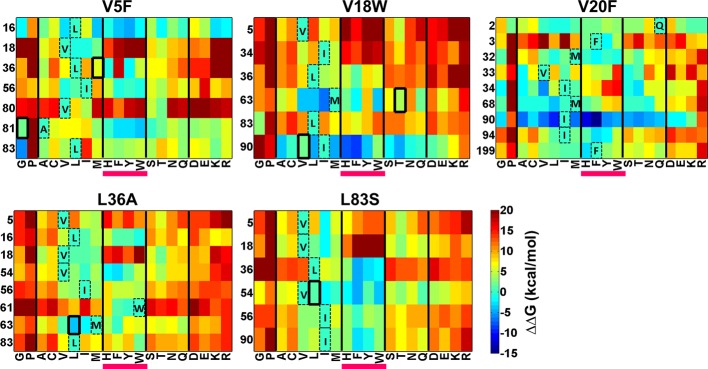
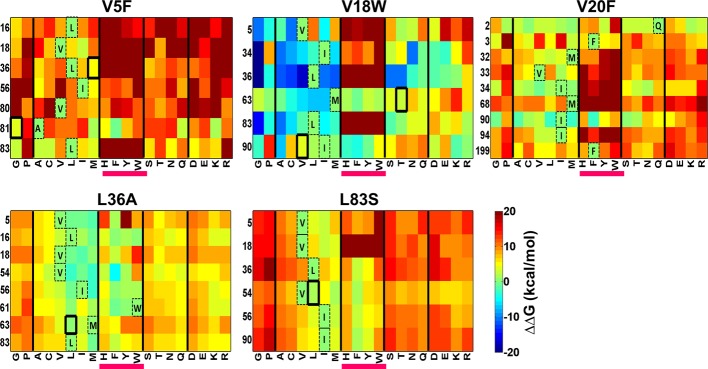
Figure 8. Heatmaps showing calculated values of ∆∆Gfolding using Rosetta for double mutants of CcdB.
All 19 mutations (X-axes) were made at positions (Y-axes) whose side chain centroids are within 7 Å of the side chain centroid of the corresponding parent inactive mutant. The parent inactive mutants are indicated in bold on the top of each heatmap. For example, the bottom left corner of the first panel represents the ∆∆G value for the (V5F, L83G) (Parent inactive mutant, suppressor) pair. Position 199 (98+101) in the V20F heatmap refers to residue 98 of the other protomer. Wild type residues are shown in dashed boxes in single letter code. Experimentally obtained suppressors are indicated by thick black boxes. Double mutants showing negative values of ∆∆Gfolding (blue shades) are ones where the putative suppressor mutation is predicted to have a stabilizing effect on the inactive mutant. Aromatic substitutions are underlined in magenta. Residues on X-axis are grouped into the following classes, separated by thick vertical lines: (G,P), aliphatic (A,C,V,L,I,M), aromatic (H,F,Y,W), polar (S,T,N,Q) and charged (D,E,K,R).Similar analysis was performed using FoldX (Figure 8—figure supplement 1).