Figure 7. Effects of anchoring COPI or COPII on Golgi organization.
(A) Anchoring COPI leads to association of early and late Golgi markers. A strain carrying the OM45-FKBPx4 anchor was transformed to express the early Golgi marker GFP-Vrg4 and the late Golgi marker Sec7-DsRed. A derivative strain also expressed Sec21-FRBx2 to anchor COPI. Cells were grown and imaged as in Figure 1, except that the confocal images were deconvolved. “+ Rap” indicates a 10-min treatment with 1 μg/mL rapamycin prior to imaging. Scale bar, 2 μm. (B) Anchoring COPII does not lead to association of early and late Golgi markers. The experiment was performed with rapamycin addition as in (A), except that the strain expressed Sec31-FRBx2 to anchor COPII, and deconvolution was omitted. Similar results were seen when COPII was anchored to mitochondria by incubating with rapamycin for 10 min as in the figure, or for 20 min (data not shown).
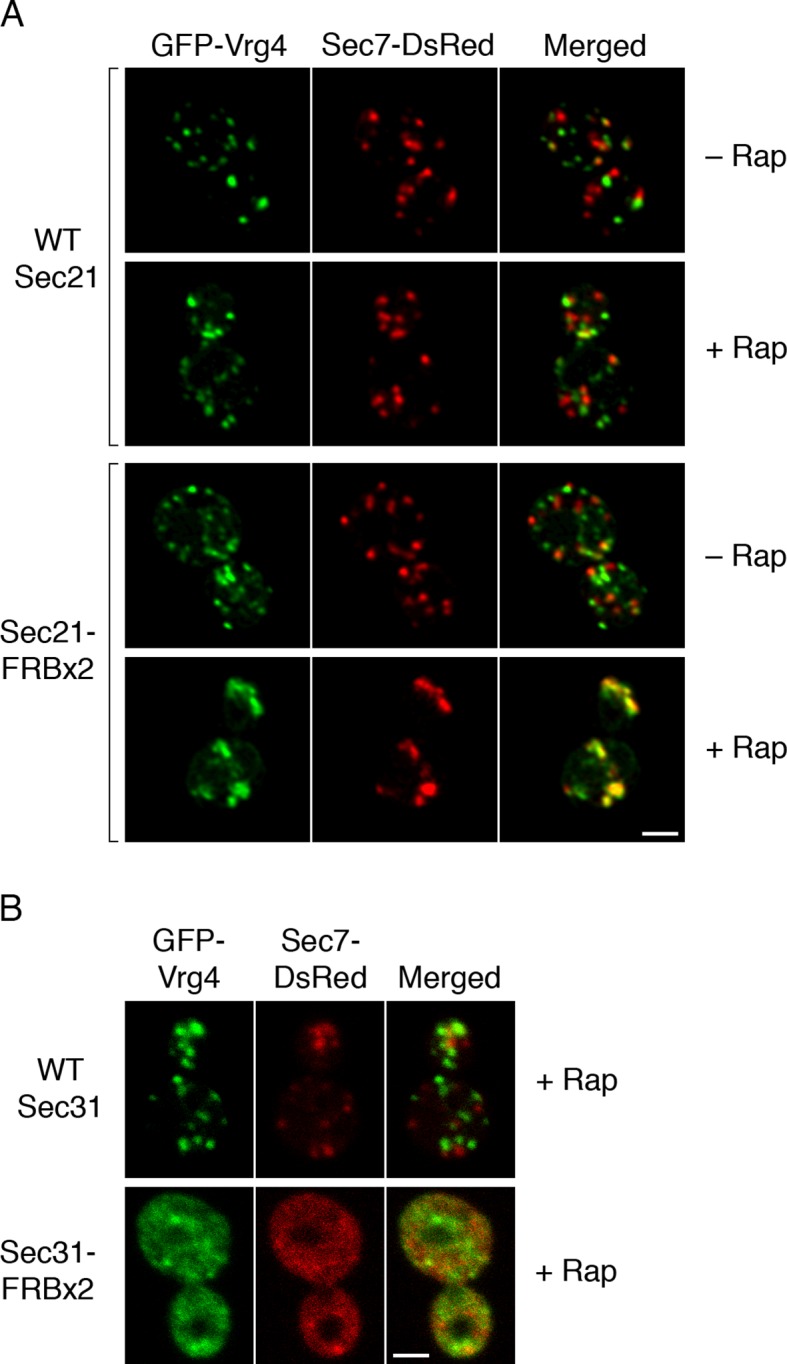
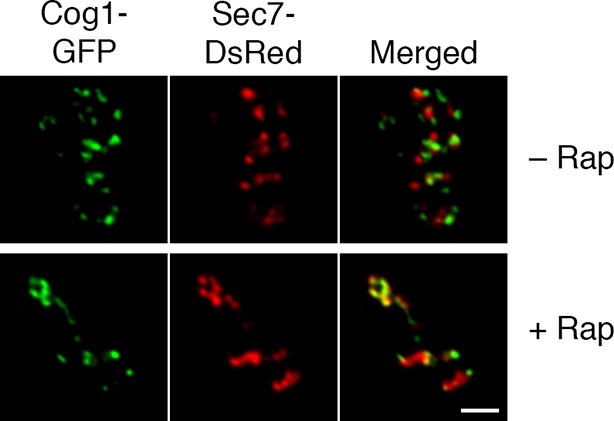
Figure 7—figure supplement 1. Formation of hybrid Golgi structures with a ribosomal anchor.
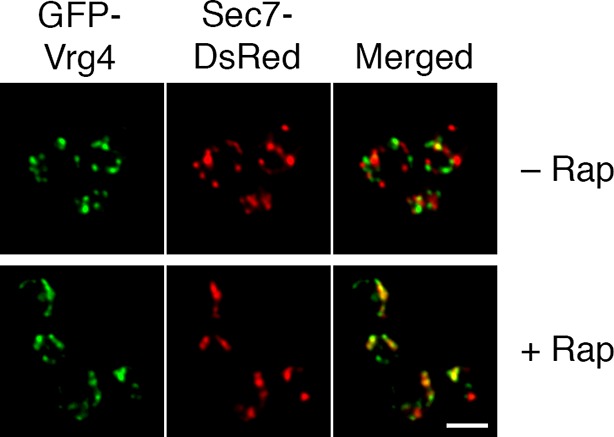
Figure 7—figure supplement 2. Visualization of hybrid Golgi structures with an alternative early Golgi marker.