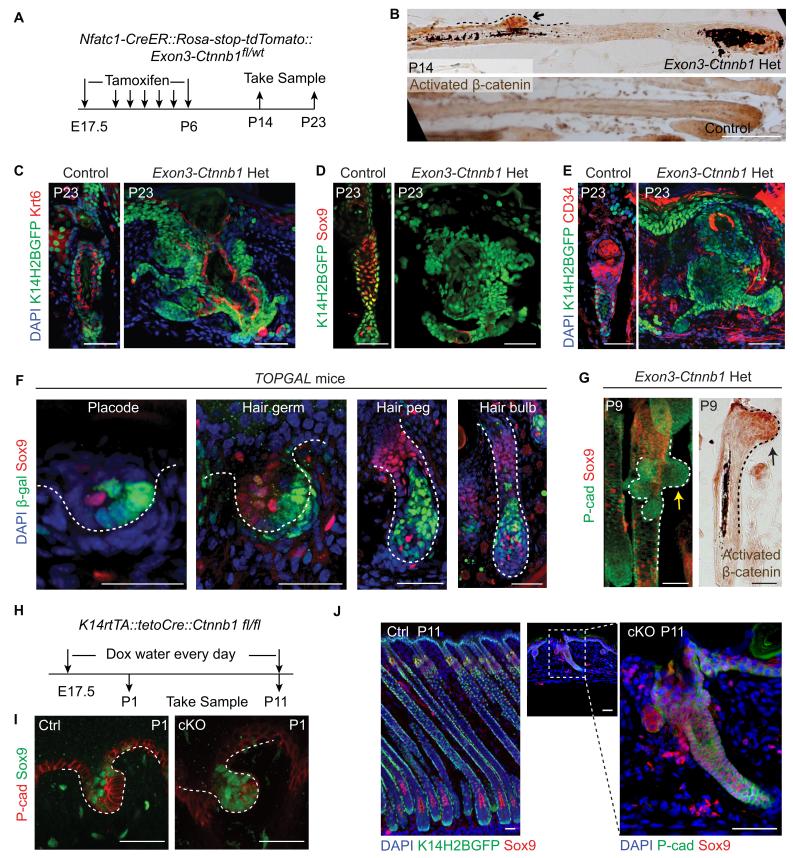
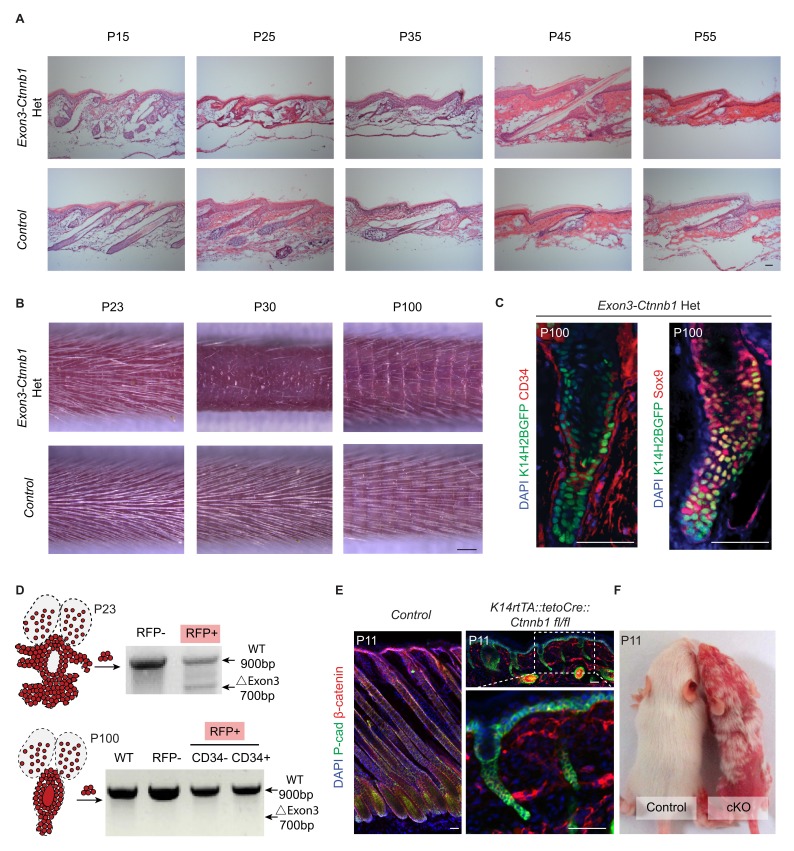
Figure 5. Elevated Wnt/β-catenin signaling abolishes hair follicle stem cell specification and suppresses Sox9 expression in hair follicles.
(A) Diagram of the experiments using Nfatc1-CreER::Rosa-stop-tdTomato::Exon3-Ctnnb1fl/wt mice. (B) Nuclear β-catenin staining indicates successful activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in upper hair follicle. (C–E) Abolished bulge niche formation and hair follicle stem cell specification in exon3-Ctnnb1 Het HFs compared to WT HFs. Krt6 (C) is a marker for inner layer bulge cells serving as a niche that can maintain quiescence for outer layer HFSCs. Sox9 (D) and CD34 (E) are adult hair follicle stem cell markers. (F) Wnt/β-catenin signal responsive cells, represented by β-gal positive cells in TOPGAL mice, do not express Sox9 during normal development. (G) Activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling suppresses Sox9 expression in vivo. The arrows point to protrusions resulting from elevated Wnt/β-catenin signaling in exon3-Ctnnb1 Het HFs. (H) Diagram of the experiments using K14-rtTA::teto-Cre::Ctnnb1fl/fl mice. β-catenin is conditionally deleted in epithelial cells by feeding mice with Doxycyclin from E17.5 to P11. Samples were taken at P1 and P11. (I–J) Loss of Wnt/β-catenin signaling leads to expanded Sox9 expression in HFs at both the hair germ stage (I) and in postnatal skin (J). Scale bars: 50 μm.