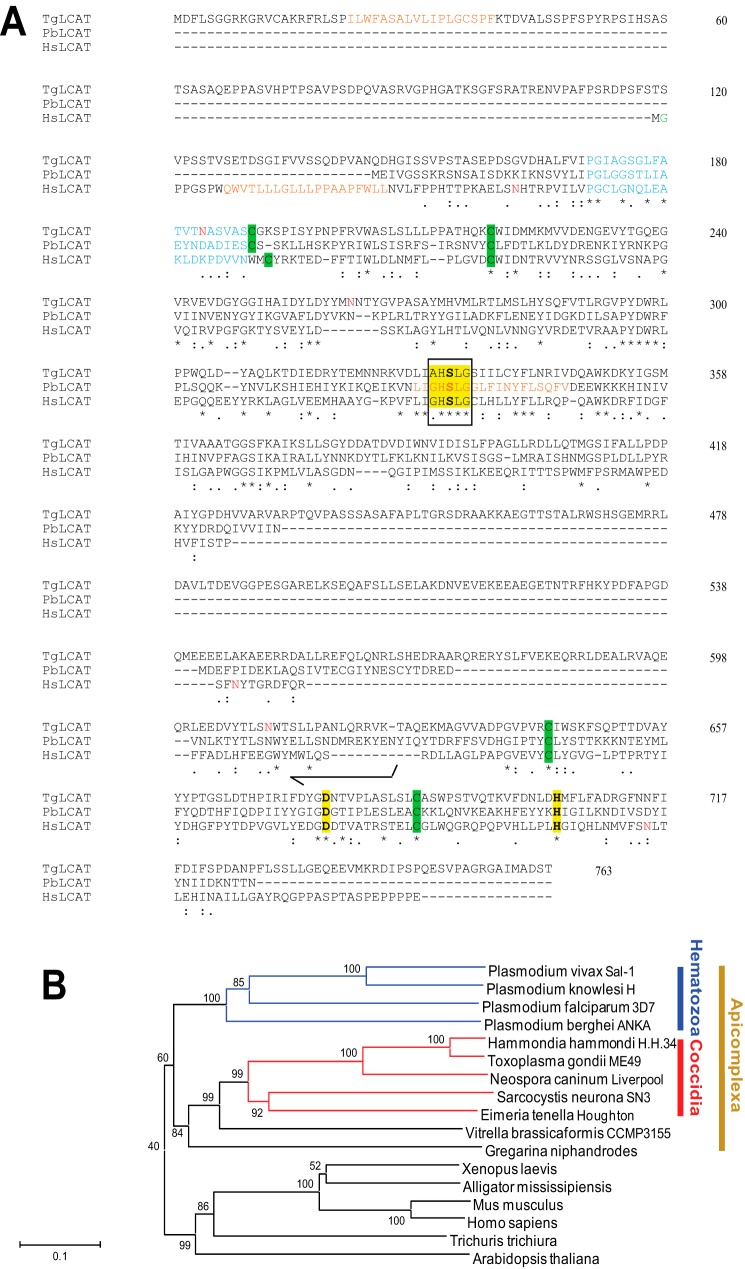
FIGURE 1.
Comparison of sequences of the predicted ORF of LCAT from T. gondii and other organisms and molecular phylogeny of LCAT proteins. A, alignment of the primary sequences of TgLCAT, P. berghei LCAT (PbLCAT; PBANKA_112810), and human LCAT (HsLCAT; AAB34898.1). Identical amino acids are indicated by asterisks. The conserved (G/A)XSXG pentapeptide sequence of the serine lipase family is boxed; the carboxyesterase active-site serine motifs and cysteine residues for potential disulfide linkages are highlighted in yellow and green, respectively; the lid region is shown in blue; potential hydrophobic regions are indicated in brown; N-linked glycosylation sites are in red; and N-myristoylation site is in green. B, sequence relationships among LCAT family proteins. Unrooted phylogenetic tree of the LCAT family proteins constructed using neighbor joining analysis. Numbers at the branch nodes represent bootstrap values (as percentages) obtained in 1,000 replications. Branch lengths indicate the number of amino acid differences.