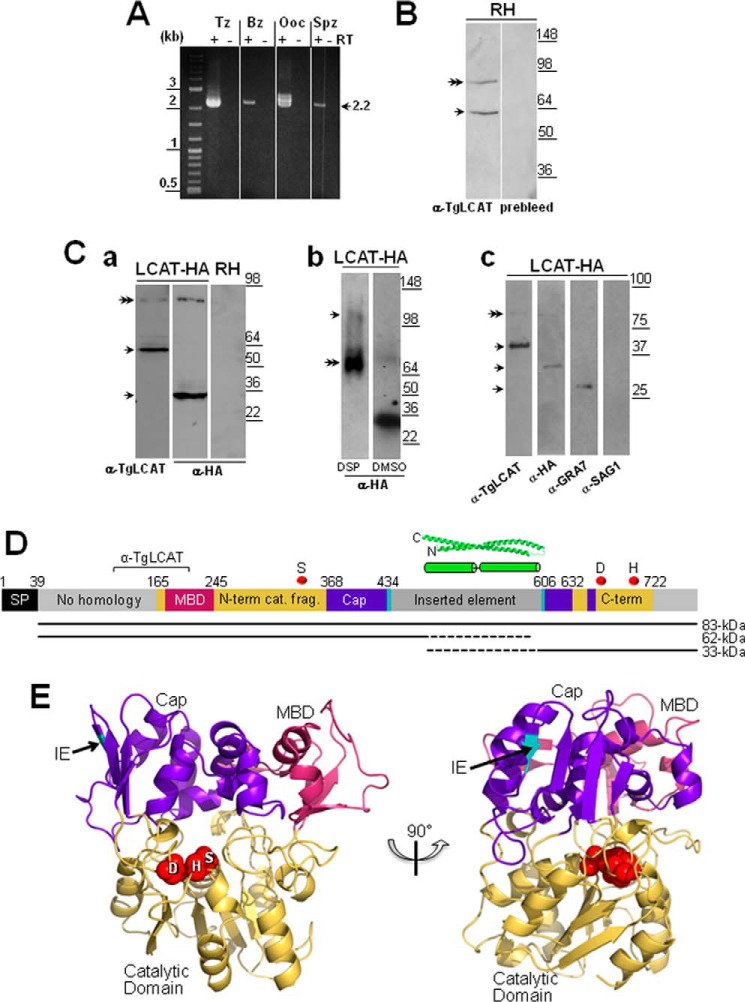
FIGURE 2.
TgLCAT expression and secretion by T. gondii. A, transcriptional profiles of lcat in tachyzoites (Tz), bradyzoites (Bz), partially sporulated oocysts (Ooc), and sporozoites (Spz). Expression of lcat transcripts from all parasite stages was assayed by RT-PCR. To verify the absence of genomic DNA contamination, RT-PCRs were set up in duplicate with (+) and without (−) reverse transcriptase (RT). B, expression of TgLCAT. Immunoblots on parasite lysates separated by SDS-PAGE and probed with anti-TgLCAT antibodies reveal two bands, one corresponding to the predicted size of TgLCAT (double arrow) and the other one corresponding to cleaved product of the protein. No signal on immunoblots was observed on these lysates probed with preimmune serum. C, secretion of TgLCAT. Panel a, immunoblots on lysates of transgenic parasites expressing LCAT-HA separated by SDS-PAGE and probed with either anti-TgLCAT or anti-HA antibodies show two forms of TgLCAT products with different sizes of peptides (single arrows) and TgLCAT full-length (double arrow). Panel b, immunoblots of lysates of transgenic parasites expressing LCAT-HA after intracellular cross-linking of TgLCAT fragments using DSP, separation by SDS-PAGE, and probing with anti-HA antibodies show full-length TgLCAT (double arrow) and an upper band at 105 kDa absent from lysates under control conditions (DMSO). Panel c, immunoblots of material secreted by transgenic parasites expressing LCAT-HA separated by SDS-PAGE and probed with anti-TgLCAT and anti-HA antibodies show stronger bands corresponding to LCAT fragments compared with a weaker band for full-length protein (double arrow). Parasite-secreted material was also probed with antibodies against GRA7 (positive control) and against SAG1 (control for parasite cell integrity). D, schematic illustration of TgLCAT. Predicted domain structure of TgLCAT is shown with putative signal peptide (SP), membrane-binding domain (MBD) based on homology with human LPLA2, N-terminal catalytic fragment (N-term cat. frag.), cap domain (Cap), inserted element (IE), and C-terminal catalytic fragment (C-term). Numbers above the illustration indicate amino acid position at the beginning of select domains. Position of the recombinant polypeptide used to immunize rats for anti-TgLCAT (α-TgLCAT) is indicated. Positions of catalytic residues SDH are indicated with red spheres. A putative coiled-coil domain within the inserted element is shown based on the highest scoring ab initio model from I-TASSER. The precursor TgLCAT species and putative proteolytic fragments are indicated as black lines below the schematic, with dashed lines indicating the estimated region of proteolysis. E, structural model of TgLCAT. Model was constructed with Phyre2, which identified human LPLA2 (Protein Data Bank code 4X91) as the highest scoring template for threading. Domains are colored according to the published structure of human LPLA2 (34). The position of the inserted element is indicated with an arrow, with the two flanking amino acid backbone residues shown in cyan. Catalytic residues, including their side changes, are shown as spheres and labeled with the single letter designations for the corresponding amino acids. The image on the right is viewed from the perspective of the membrane, with the catalytic pocket shown centrally. The left image is rotated 90° from the right image.