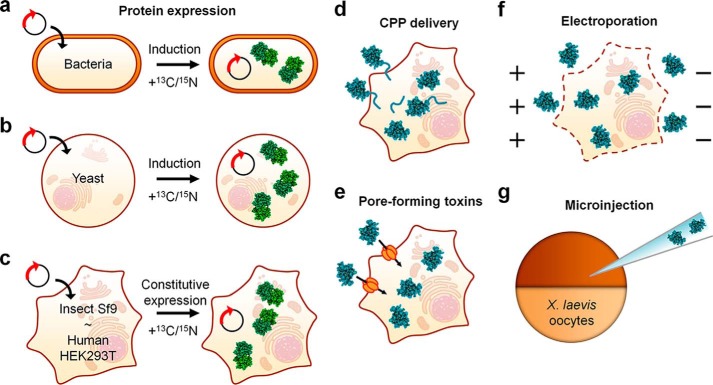
FIGURE 1.
Overview of the existing sample preparation approaches for in-cell NMR. a–c, isotopically labeled proteins can be expressed (green) in bacterial cells (a) and yeast cells (b) by transforming the cells with expression vector(s) encoding the protein(s) of interest; proteins can be expressed in insect and human cells (c) by transfecting the cells with constitutive expression vectors. Isotopically enriched nutrients are added after induction/transfection. d–f, purified labeled proteins (blue) can be inserted in human cells by Cu,Zn-SOD1 CPP-mediated delivery (d), or by permeabilizing the cells either with pore-forming toxins (e) or via electroporation (f). g, proteins can be inserted in X. laevis oocytes by microinjection.