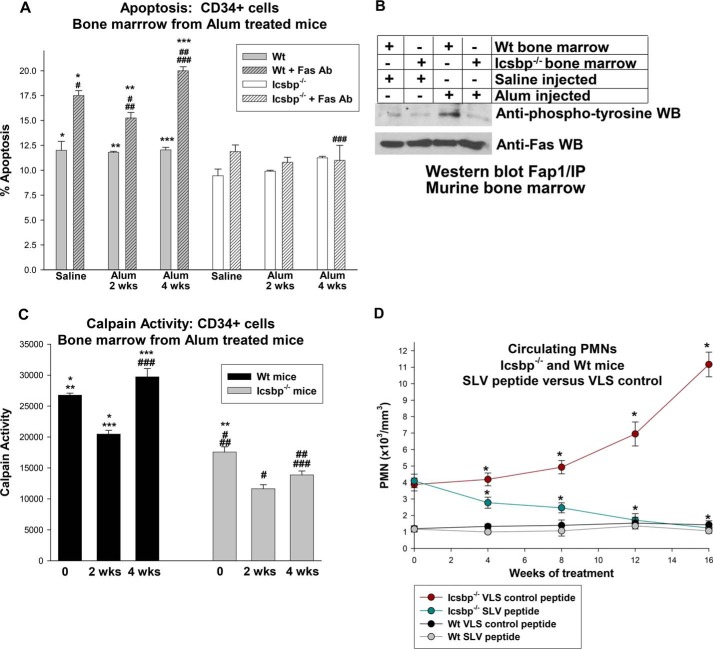
FIGURE 5.
Sustained Fas resistance and calpain-repression were observed in bone marrow progenitor cells from Icsbp−/− mice after stimulation of emergency granulopoiesis. Icsbp−/− or wild-type mice were injected with Alum to induce emergency granulopoiesis or saline as a steady-state granulopoiesis control, and bone marrow was obtained at various time points. A, Fas-induced apoptosis was significantly greater in CD34+ bone marrow cells from Alum-treated WT mice than in Icsbp−/− mice. Statistically significant differences are indicated by *, **, ***, #, ##, and ###. B, Fas phosphorylation was decreased in bone marrow progenitor cells from Icsbp−/− mice in comparison with WT bone marrow. CD34+ cells from Icsbp−/− or WT murine bone marrow were analyzed with or without G-CSF stimulation for Fas phosphorylation by immunoprecipitation/Western blotting (WB). C, calpain activity in WT bone marrow progenitor cells was increased relative to baseline 4 weeks after stimulation of emergency granulopoiesis but remained decreased in Icsbp−/− bone marrow. CD34+ cells were analyzed by calpain activity assay. Statistically significant differences are indicated by *, **, ***, #, ##, and ###. D, treatment with Fap1-blocking SLV peptide prevented progressive granulocytosis in Icsbp−/− mice but had no effect on WT mice. Mice were injected three times per week with SLV or VLS (control) peptide. Time points with statistically significant differences are indicated by *. p < 0.02 was considered statistically significant.