FIGURE 7.
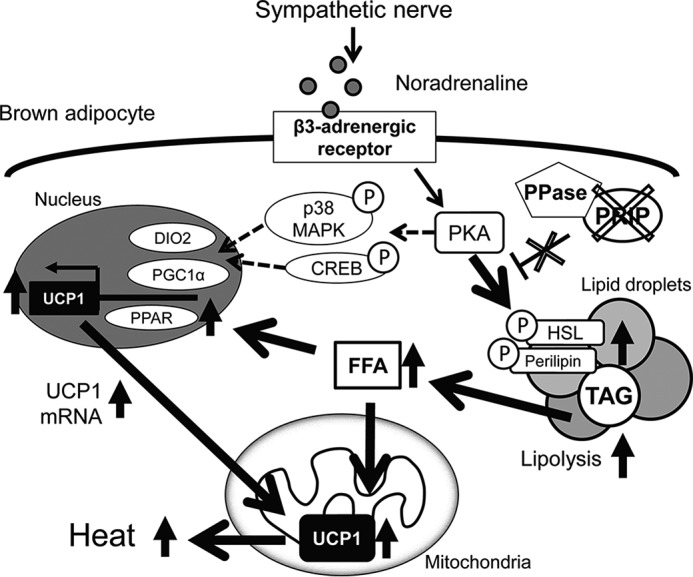
Schematic representation of the regulation of brown fat thermogenesis by PRIP. Sympathetic nerve stimulation enhances receptor-mediated PKA activation in brown adipocytes. PKA induces UCP1 activation by at least two pathways. (i) PKA facilitates the phosphorylation of HSL and perilipin, which promotes lipolysis. The resulting FFAs enhance UCP1 enzymatic activation and Ucp1 gene expression through PPAR-mediated PGC1α activation (the pathway represented by the solid arrows). (ii) PKA also induces phosphorylation of CREB and p38 MAPK, which activate PGC1α and DIO2 (represented by dashed-line arrows). Consequently, Ucp1 gene expression and activity are elevated. Our data show that Prip gene ablation (represented by the X-marks) leads to elevation of HSL and perilipin phosphorylation-mediated lipolytic cascades followed by FFA-mediated UCP1-induced heat production. Upward arrows denote up-regulation of expression or activity. Encircled Ps indicate phosphoproteins. DIO2, type II iodothyronine 5′ deiodinase; FFA, free fatty acid; PKA, cAMP-dependent protein kinase; p38 MAPK, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; PGC1α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ co-activator 1α; PPase, protein phosphatase.
