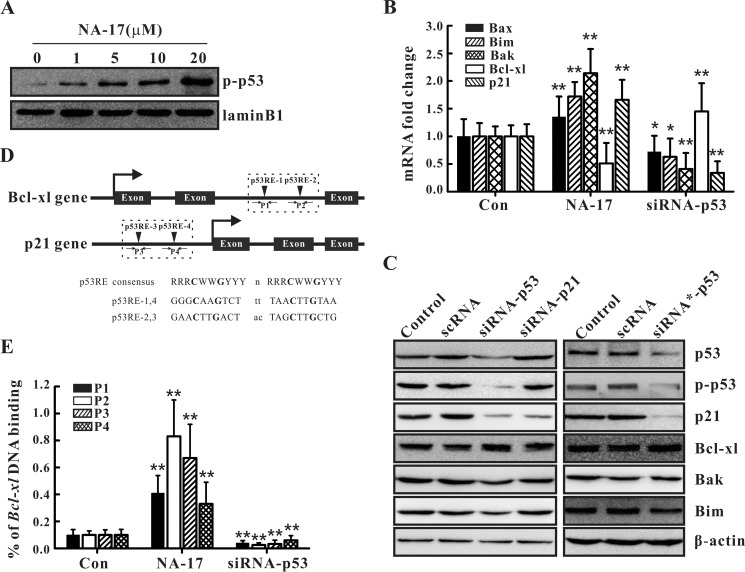
FIGURE 8.
NA-17-induced nuclear accumulation of phospho-p53 transcriptionally regulated the related targets by directly binding to DNA. A, phospho-p53 (p-p53) accumulation in cell nuclei after NA-17 treatment. NCI-H460 cells treated with NA-17 were subjected to subcellular fractionation, and immunoblotting was performed with nuclear fractions. Lamin B1 was used as the nuclear marker protein. B, quantitative real time PCR assays were performed in non-treated (control (Con)), NA-17-treated (5 μm), or p53 siRNA-treated NCI-H460 cells. C, immunoblotting analysis of p21 and the Bcl-2 family proteins after p53 siRNA or p21 siRNA treatment. D, putative p53 response elements were located in the intron of the Bcl-xl gene and in the promoter of the p21 gene. D, ChIP assays based on an anti-phospho-p53 antibody and primer pairs P1, P2, P3, or P4 were performed in non-treated, NA-17-treated (5 μm), or p53 siRNA-treated NCI-H460 cells. Error bars represent S.D.