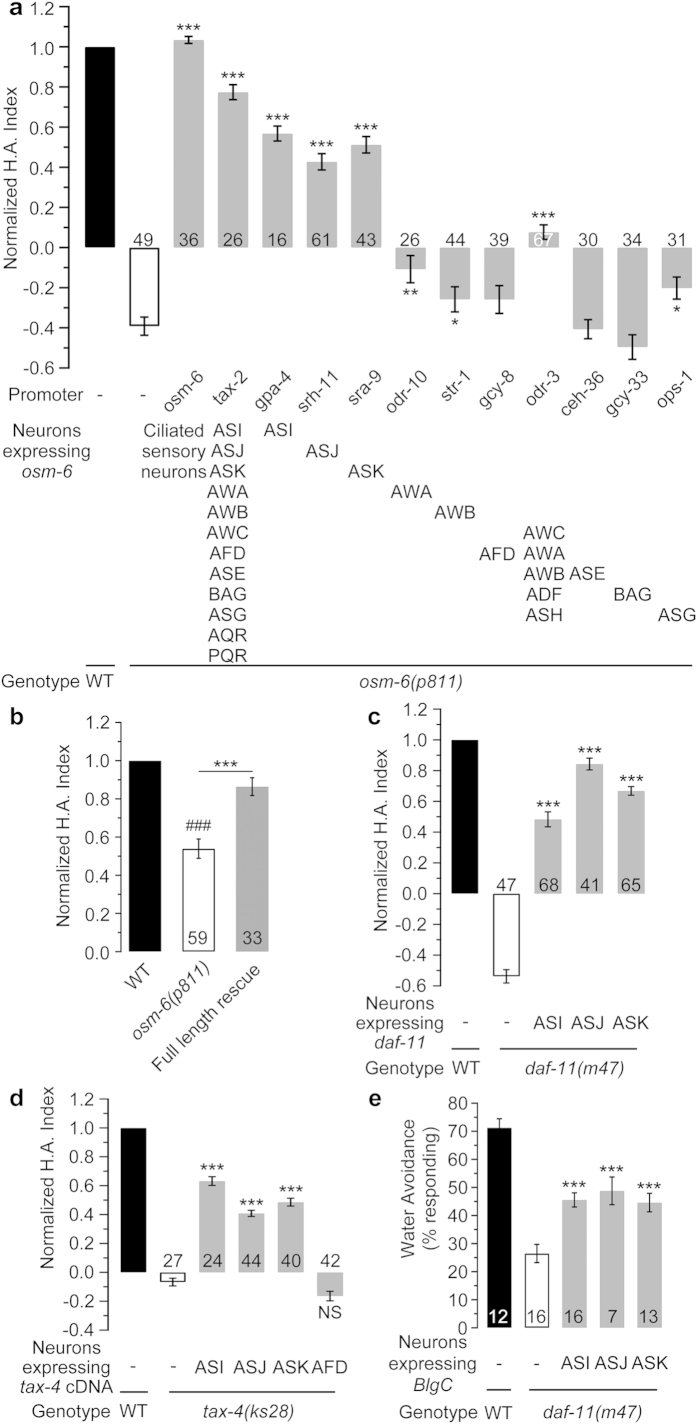
Figure 3. Identification of the hydrosensory receptor neurons.
(a) The normalised H.A. index of the osm-6(p811) mutants and neuron-specific rescued worms, as indicated by the WSA assay. (b) The normalised H.A. index of the osm-6(p811) mutants and worms rescued with the full-length osm-6 genomic DNA, as indicated by the four-quadrant agarose assay with equal concentrations of Na+. (c) The normalised H.A. indexes of the daf-11(m47) mutants and worms that were specifically rescued with the full-length daf-11 genomic DNA in the ASI, ASJ and ASK neurons, as tested by the WSA assay. (d) The normalised H.A. indexes of the tax-4(ks28) mutants and worms that were specifically rescued with the tax-4 cDNA in the ASI, ASJ, ASK, and AFD neurons, as tested by the WSA assay. (e) The artificial increase in the cytosolic cGMP levels by photo-activation of BlgC expressed specifically in the ASI, ASJ and ASK neurons remarkably rescued the hydropreference defect of the daf-11(m47) mutants, as assayed by the drop test. The data for each genotype are normalised to the corresponding wild-type N2 control, which is shown as only one bar. The number of independent tests for each genotype is indicated on the bar. Statistics: *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01 and ***P ≤ 0.001 compared to each N2 control (Student’s t-test or Mann-Whitney Rank Sum test, depending on the normality of the data distribution). The error bars indicate the SEM. WT, wild-type; H.A., hydroaversive.