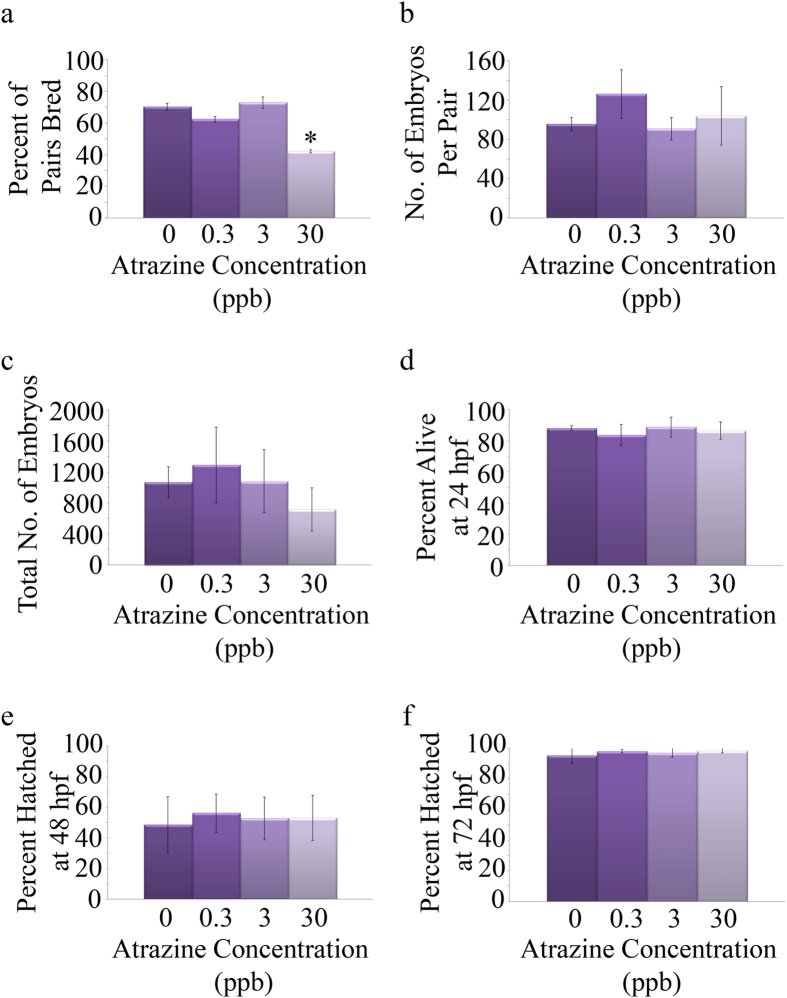
Figure 1. Assessment of embryonic atrazine exposure on adult zebrafish reproductive function and offspring viability.
Adults were individually paired in mating experiments to assess mating success (16 pairs from each of the 4 biological replicates). Average number of pairs that bred was decreased in the group exposed to 30 ppb atrazine during embryogenesis (a). There were no significant differences observed for the number of embryos per pair or the total number of embryos per treatment (b,c, respectively). In addition, no significant changes were observed in mortality of the offspring (d) or in hatching rates at 48 and 72 hpf (e,f, respectively). Error bars are expressed as ± SD. (*p < 0.05).