Fig. 4.
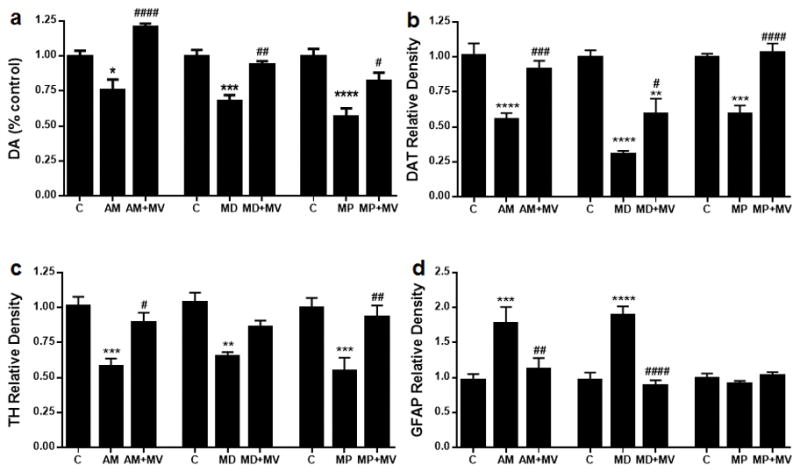
Effects of MDPV (4′ – 30 mg/kg) on amphetamine (4′ – 5 mg/ kg)-, 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) (4′ – 20 mg/kg)-, and MPTP (2′ – 20 mg/kg)-induced neurotoxicity to DA nerve endings. Mice were treated with MDPV (MV; 4′ – 30 mg/kg) in combination with amphetamine (AM; 4′ – 5 mg/kg), MDMA (MD; 4′ –20 mg/kg) or MPTP (MP; 2′ – 20 mg/kg) and the levels DA (a), dopamine transporter (DAT) (b), tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) (c), and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) (d) were determined 2 days after treatment. Controls were injected with physiological saline on the same binge schedule used for all drugs. DA levels were determined by HPLC and are reported as % control. Relative pixel densities for immunoblots of DAT, TH and GFAP were quantified using ImageJ, normalized to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and expressed as relative band density by comparison with the respective control. Data are mean ± SEM for n = 5–6 mice per group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 and ****p < 0.0001 by comparison with untreated controls. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 and ####p < 0.0001 by comparison with AMPH, MDMA or MPTP alone. Specific details of all statistical comparisons for the data in this figure are included in Tables S3 and S4.
