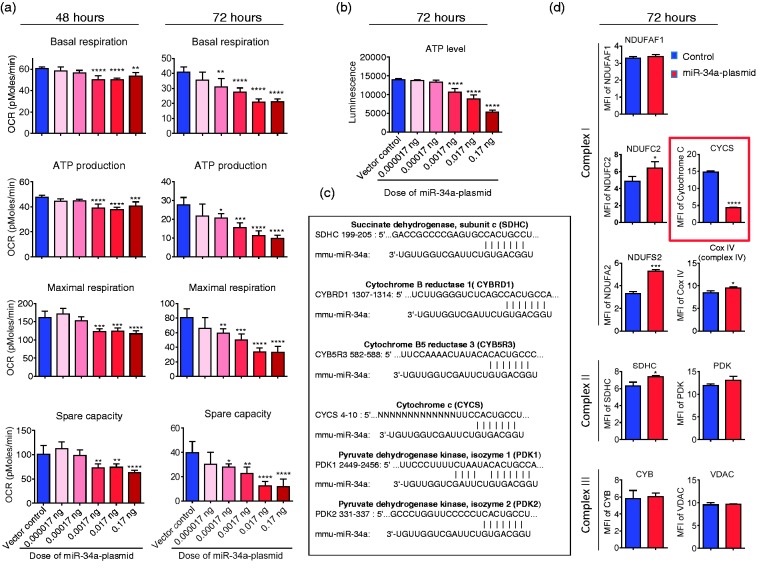
Figure 2.
Overexpression of mir-34a reduces mitochondrial function and decreases CYC level in cerebrovascular endothelial cells. (a) Basal respiration, ATP production, maximal respiration, and spare capacity were calculated from the bioenergetics functional assay at post-transfection 48 and 72 h (raw data in Supplementary Figure 3). Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 5). 1-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Tukey’s test. (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001). (b) ATP level was measured at 72 h post-transfection. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 5). 1-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Tukey’s test. (****, P < 0.0001). (c) Bioinfomatic analysis of miR-34a-targeting candidates related to mitochondria. (d) Flow cytometry analysis of mitochondrial specific proteins for complex I proteins (NDUFAF1, NDUFC2 and NDUFS2), complex II protein (SDHC), complex III protein (CYB), complex IV protein (CYC oxidase, Cox IV), cytochrome c (CYCS), pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (PDK), and voltage-dependent anion channel protein (VDAC) at 72 h post-transfection. CYC level was significantly lower in the cells that were transfected with the miR-34a plasmid. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3) and analyzed by Student’s t-test, *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. Results are representative of three independent experiments.