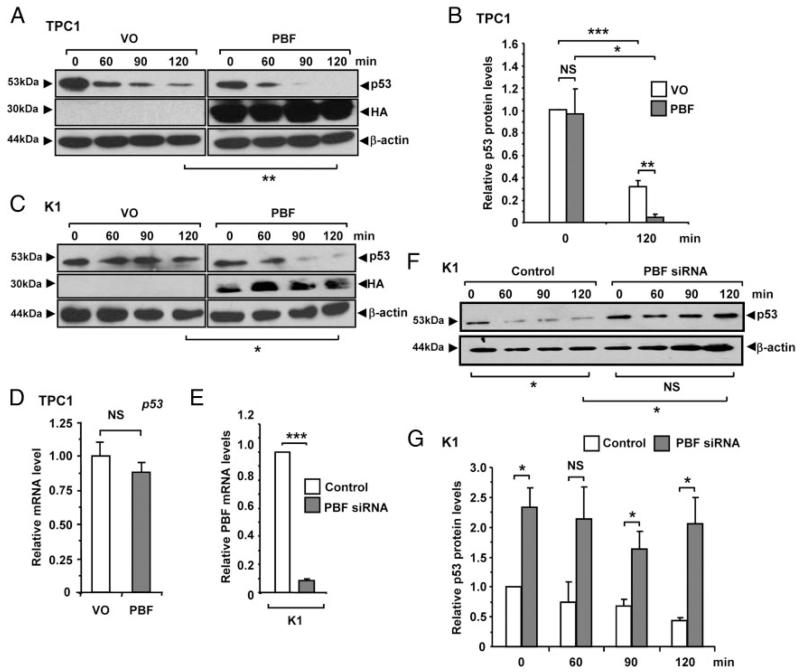
Figure 2.
PBF decreases p53 intracellular stability. Representative Western blot analysis of p53 in (A) TPC1 and (C) K1 cells transfected with either vector only (VO) or PBF and then lysed at indicated times post-treatment with 100 μM anisomycin. Detection of HA epitope was used to monitor transfection. Mean p53 protein levels relative to β-actin in TPC1 cells are shown in (B) from 3 independent experiments. D, Relative mRNA levels of p53 in TPC1 cells transfected with either VO or PBF. E, Relative mRNA levels of PBF in K1 cells transfected with either PBF-specific or control siRNA for 72 hours at a concentration of 100 nM. F, Representative Western blot analysis of p53 in K1 cells transfected with either PBF-specific or control siRNA and then lysed at indicated times post-treatment with 100 μM anisomycin. G, Quantification of p53 protein levels relative to β-actin from p53 half-life experiments in K1 cells transfected with either PBF-specific or control siRNA. Data presented as mean p53 levels ± SE from 3 independent experiments. *, P < .05; ***, P < .001; NS = not significant.