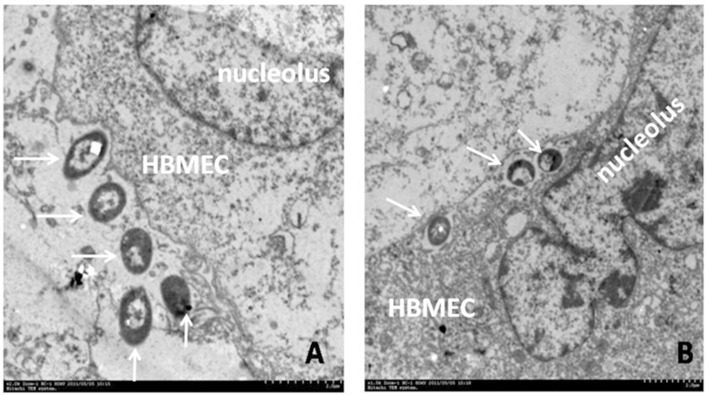
Figure 2.
Bacterial adhesion to and invasion of human BMEC (HBMEC). Transmission Electron Microscopy shows meningitic E. coli K1 (E44) adhesion to (A) and invasion across (B) human BMEC. E. coli closely contacted the human BMEC membrane and elicited its own uptake at the site of infection (A). Intracellular bacteria are identified in membrane-bound vacuoles after 30 min of incubation (B). Arrows indicate the processes of bacterial adhesion (A) and subsequent invasion (B).