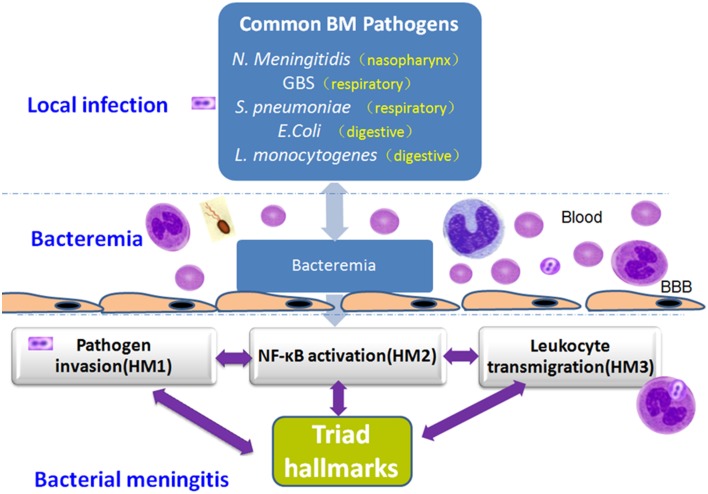
Figure 5.
Mechanistic triad of bacterial meningitis (BM): Pathogen penetration, NF-kB activation and leukocyte transmigration that occur at the BBB. BM caused by pathogens usually begins with local tissue adhesion and colonization of the potentially meningitic microorganisms. After successful traversal of the local tissue barrier (e.g., the gut barrier for enteric pathogens), a high degree of bacteremia is required for penetration of pathogens across the BBB to cause meningitis. NF-kB activation, a mechanistic link, contributes to both pathogen penetration and leukocyte transmigration across the BBB. The NF-kB signaling pathway can serve as a drug-discovery platform.