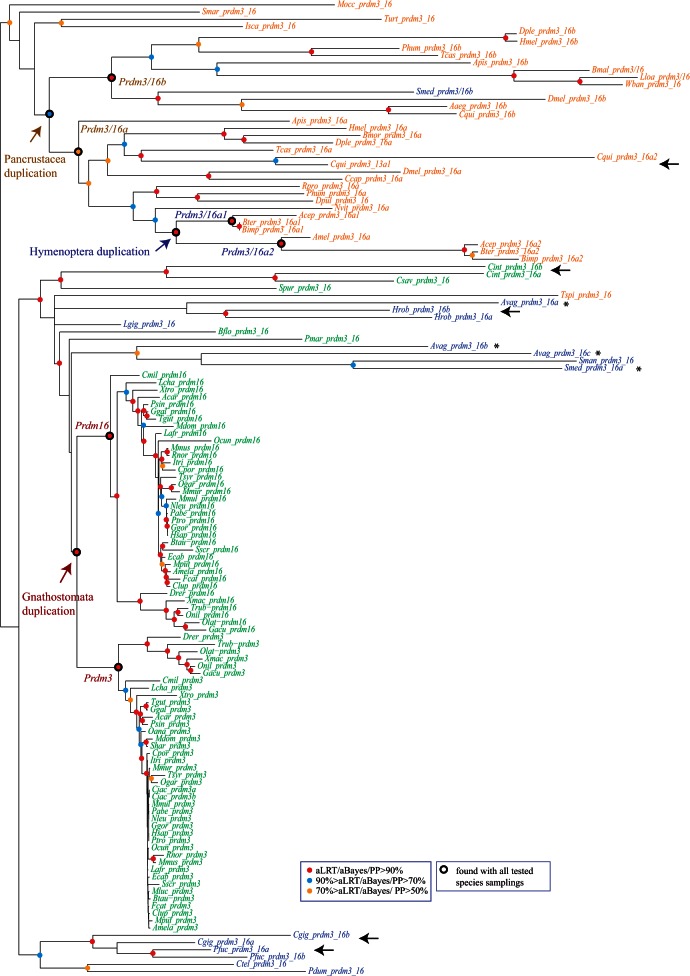
Fig. 6.
Phylogenetic analysis of the Prdm3/16 subfamily. An ML tree is shown. Midpoint rooting has been used. A similar tree topology has been obtained by BI. Statistical supports (aLRT and aBayes values for ML; posterior probabilities for BI) are indicated on the nodes by color circles (color code is indicated in the figure). Nodes without color circles are not statistically supported and/or not congruent between ML and BI methods. Species names are abbreviated using the first letter of the genus name followed by the three first letters of the species name. All abbreviations can be found in table 1. Black arrows indicate pairs of paralogs that are closely related in the phylogenetic tree, whereas asterisks denote paralogs that are not closely associated in the phylogenetic tree. Duplications that likely occurred in Gnathostomata, Pancrustacea, and Hymenoptera are indicated. Nodes that define the monophyletic groups that allowed to position these duplications are also highlighted (Prdm3/Prdm16; Prdm3_16a/Prdm3_16b; Prdm3_16a1/Prdm3_16a2). These monophyletic groups are also found in ML trees constructed with several different species samplings (sampling 1: only deuterostome genes; sampling 2: only chordate genes; sampling 3: only vertebrate genes; sampling 4: only deuterostomes and ecdysozoans; sampling 5: only protostomes; sampling 6: only ecdysozoans; sampling 7: only arthropods).