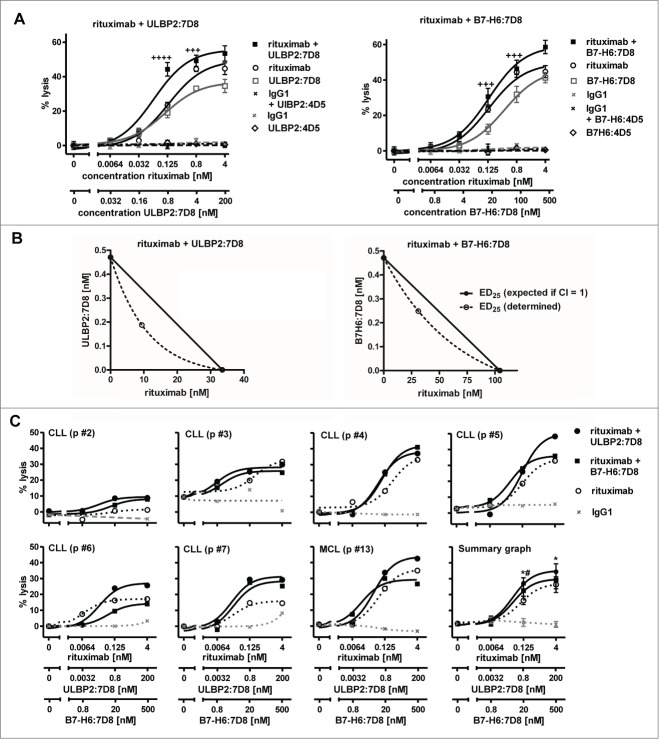
Figure 3.
Enhanced killing of patients' tumor cells by combinations of rituximab and the immunoligands. (A) Both ULBP2:7D8 (left panel) and B7-H6:7D8 (right panel) increased rituximab-mediated ADCC against freshly isolated CLL cells (CLL p #1; ++++, CI = 0.1 − 0.3; +++, CI = 0.3 – 0.7). (B) Illustration of synergistic effects at the 25% effect level by isobolograms. (C) Cytotoxicity induced by varying concentrations of rituximab alone or in combination with either ULBP2:7D8 or B7-H6:7D8 against a panel of tumor cell samples. NK cells from healthy donors were applied as effector cells (E:T cell ratio = 20:1). Data are presented as mean percentage of lysis from triplicate determinations. Data acquired with different tumor samples were analyzed in a summary graph for statistical analysis. (* and # indicate statistical significant differences between rituximab as single agent or combined with either ULBP2:7D8 or B7-H6:7D8, respectively. p, patient).